Public:Graphical User Interface: Difference between revisions
m (→SB Presets) |
m (→SB Presets) |
||
| Line 512: | Line 512: | ||
|Object detection | |Object detection | ||
| | | | ||
* OD | * OD based on a trained neural network allows to detect people, equipment, drones, artificial structures from different angles and at different distances, highlighting them on the screen, measuring distance, azimuth, elevation, height above the ground, speed, course destination and geolocation, as well as displaying them on the navigation grid | ||
* | * launches the CVC app in the CRW window by default at the same time as the last used front camera preset (FHD, SWIR, LWIR, SLV, MXV1-4) | ||
* | * if necessary, prompts the user to select another front camera preset, as well as launch Computer Audition and Radio Detection presets to refine detection results | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* | * can be run simultaneously with MD, FD, FR, OCR, HSTD presets | ||
|- | |- | ||
|MD | |MD | ||
|Motion detection | |Motion detection | ||
| | | | ||
* MD | * MD helps to detect moving objects, people and evehicles ignoring the flights of birds and insects, tand he movement of clouds. MD mode is recommended to be used in conjunction with Radio Frequency Drone Detection (RFDD) and Computer Audition Detect noises of aircraft motor (DAM) preset | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be run simultaneously with OD, FD, FR, OCR, HSTD presets | |||
|- | |- | ||
|FD | |FD | ||
|Facial detection | |Facial detection | ||
| | | | ||
* FD | * FD incl. using LWIR camera sensor and trained neural network helps to detect people's faces | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be run simultaneously with OD, MD, FR, OCR, HSTD presets | |||
|- | |- | ||
|FR | |FR | ||
|Facial recognition | |Facial recognition | ||
| | | | ||
* FR | * FR using a neural network in the presence of an exchange with the server allows to recognize people's faces for identification (part of the database can be stored on a local drive) | ||
* | * always executed at the same time as the FD preset | ||
* | * can be run simultaneously with OD, MD, OCR, HSTD presets | ||
|- | |- | ||
|OCR | |OCR | ||
|Optical character recognition | |Optical character recognition | ||
| | | | ||
* OCR | * OCR allows to recognize text and other graphic characters for subsequent translation and documentation | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be run simultaneously with presets OD, MD, FD, HSTD | |||
|- | |- | ||
|HSTD | |HSTD | ||
|Heat and smoke trace detection | |Heat and smoke trace detection | ||
| | | | ||
* HSTD | * HSTD helps detect aircraft and missile trajectories, artillery and mortar fire from closed masked positions | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be run simultaneously with presets OD, MD, FD, FR | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="5" |[[File:Computer Hearing modes@4x.png|left|frameless|26x26px]] | | rowspan="5" |[[File:Computer Hearing modes@4x.png|left|frameless|26x26px]] | ||
| rowspan="5" |Computer Audition modes | | rowspan="5" |Computer Audition modes | ||
'' | ''AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset)'' | ||
|DAM | |DAM | ||
|Detect noises of aircraft motor | |Detect noises of aircraft motor | ||
| | | | ||
* DAM | * DAM, unlike DHUM, works only with patterns of aerodynamic, electromechanical and mechanical noise, using a trained neural network, isolating and amplifying sounds and noises that are most likely associated with the operation of drones, helicopters, turboprops and jet aircraft | ||
* | * this preset allows to focus on likely threats from the air and determine the direction of the source of sound waves | ||
* DAM | * DAM is recommended to be used in conjunction with Radio Frequency Drone Detection (RFDD) and Computer Vision Motion Detect (MD) | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be played simultaneously with ENAT, ECHO, DHUM, STHR presets | |||
|- | |- | ||
|ENAT | |ENAT | ||
|Exclude sounds of nature | |Exclude sounds of nature | ||
| | | | ||
* ENAT | * ENAT sequentially selects the sounds and noises of nature (wind, rustle of leaves, birdsong, water sound, etc.) in several frequency ranges with the help of filters, then using a trained neural network to select patterns for final filtering | ||
* | * this preset allows to focus on the sounds and noises associated with human activity | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be played simultaneously with presets DAM, ECHO, DHUM, STHR | |||
|- | |- | ||
|ECHO | |ECHO | ||
|Eliminate echo | |Eliminate echo | ||
| | | | ||
* ECHO | * ECHO, using built-in algorithms, allows to detect primary and reflected sound waves in order to correct the direction of the source of sound waves when other presets are working | ||
* | * prompts the user when to enable this preset if one of the other presets is already enabled | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be played simultaneously with DAM, ENAT, DHUM, STHR presets | |||
|- | |- | ||
|DHUM | |DHUM | ||
|Detect noises of human activity | |Detect noises of human activity | ||
| | | | ||
* DHUM | * unlike ENAT, DHUM works in the opposite direction, using a trained neural network, to isolate and amplify sounds and noises that are most likely associated with human activity (tire friction, footstep sounds, stone friction, radio speaker sound, engine sounds, electromechanical noise, coughing, sneezing, speech, etc.) | ||
* | * this preset highlights these patterns of audio frequencies, amplifies them, while attenuating the sound level of the environment | ||
* | * this preset allows to focus on the sounds and noises associated with human activities, and determine the direction of the source of sound waves | ||
* | * this preset also uses the method of acoustic location and determining the coordinates of the enemy battery based on the sound of firing its guns (or mortars, or rockets)<ref>Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:Artillery_sound_ranging|Artillery sound ranging]]</ref> | ||
* | * uses local pattern library only | ||
* can be played simultaneously with DAM, ENAT, ECHO, STHR presets | |||
|- | |- | ||
|STHR | |STHR | ||
|Limit sound threshold | |Limit sound threshold | ||
| | | | ||
* STHR | * STHR assists the user in variable high ambient sound pressure conditions by dynamically reducing the maximum level by ∆ 80 dB SPL to 15-85 dB SPL | ||
* STHR | * STHR is synchronized with the electromechanical sound dampers in the headphone design | ||
* | * can be played simultaneously with DAM, ENAT, ECHO, DHUM preset | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="5" |[[File:Radio Detection modes@4x.png|left|frameless|20x20px]] | | rowspan="5" |[[File:Radio Detection modes@4x.png|left|frameless|20x20px]] | ||
| rowspan="5" |Radio detection modes | | rowspan="5" |Radio detection modes | ||
'' | ''AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset)'' | ||
|IFF | |IFF | ||
|Identification Friend-or-Foe | |Identification Friend-or-Foe | ||
| | | | ||
* IFF | * IFF uses a transponder (transmitter-responder) Identification Friend-or-foe system, which in response to an encrypted interrogation signal received on one frequency, sends an encrypted message packet on another frequency containing the confirmation "Friend", Id, callsign and position | ||
* | * when used simultaneously with one of the "Stealth" modes presets, IFF will send a response message at different frequencies, in different networks, and with different power (for a limited distance) or will not send a message at all | ||
* | * a transponder with a specified interval at certain frequencies periodically generates and sends interrogation signals to an indefinite circle of people for registration and display on the navigation grid of one of the screens of user positions, with confirmation "Friend" | ||
* | * interrogation signals sent via an omnidirectional antenna or a directional antenna (the omnidirectional pattern can be limited by a reflective array or a software-defined antenna can be used) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|RDF | |RDF | ||
|Radio Direction Finding<ref name=":3">Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:Direction_finding|"Radio direction finding"]]</ref> | |Radio Direction Finding<ref name=":3">Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:Direction_finding|"Radio direction finding"]]</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
* RDF | * RDF applies the radio direction finding of received radio frequencies that are identified as potentially threatening (radar, EW&SIGINT, ECM systems) or identified as the source of an RF carrier (analog or digital signal) for communication | ||
* | * using triangulation in collaboration with a similar device of another user in the P2P network (at a short distance with it) determines the direction and distance to the radio signal source | ||
* | * without the help of another user's device or software-defined antenna determines only the direction (course) to the radio signal source | ||
* | * commonly used after running the SDR Scan (SDRS) app to first identify the characteristics of the radio signal and not unmask itself unnecessarily | ||
* | * in accordance with the current rules and restrictions, the mission can initiate a task for the above IFF app if the interrogation signal is not sent to identify the source of the signal by other methods or with the help of other persons | ||
* | * in conditions of distortion or jamming of radio signals of navigation satellite systems, it is used for radio navigation using terrestrial radio beacons operating in other frequency bands, including FM, TV and mobile radio broadcasting bands | ||
|- | |- | ||
|RFDD | |RFDD | ||
|Radio Frequency Drone Detection<ref name=":0">AARTOS, [https://drone-detection-system.com/sensor-types-overview/detection-rf/#:~:text=AARTOS%E2%84%A2%20RF%20Detection.,by%20comparing%20different%20frequency%20patterns. "RF Drone Detection"], [https://drone-detection-system.com/sensor-types-overview/detection-rf/#antennas "Antennas"]</ref> | |Radio Frequency Drone Detection<ref name=":0">AARTOS, [https://drone-detection-system.com/sensor-types-overview/detection-rf/#:~:text=AARTOS%E2%84%A2%20RF%20Detection.,by%20comparing%20different%20frequency%20patterns. "RF Drone Detection"], [https://drone-detection-system.com/sensor-types-overview/detection-rf/#antennas "Antennas"]</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
* RFDD enables the mode of radio frequency detector used to detect the presence of RF waves in physical transmission mediums | * RFDD enables the mode of radio frequency detector used to detect the presence of RF waves in physical transmission mediums | ||
* the system uses these RF Detectors to detect drones and drone pilots | * the system uses these RF Detectors to detect drones and drone pilots | ||
* RFDD also uses AI to identify the type of threat by comparing different frequency patterns | * RFDD also uses AI to identify the type of threat by comparing different frequency patterns | ||
* the system can easily distinguish drones from common RF signals by using learned patterns and can identify almost all types of threats as well as the location of the drone pilot | * the system can easily distinguish drones from common RF signals by using learned patterns and can identify almost all types of threats as well as the location of the drone pilot | ||
* | * can use a compact omnidirectional mobile manpack antenna, a directional software-defined antenna, or a longer-range mobile portable antenna | ||
* | * has a range of 9 kHz - 8 GHz and a detection distance of up to 3 miles (conical or dome range) | ||
* | * this function displays on the navigation grid and / or on the map of the terrain of the interface screens the positions of the identified RPA (UAV) and its operator | ||
* | * RFDD mode - a special case of the RDF function, it is recommended to use it in conjunction with the Computer Vision Motion detection (MD) and Computer Audition Detect noises of aircraft motor (DAM) modes | ||
|- | |- | ||
|EODD | |EODD | ||
|Radio Frequency Explosive Ordnance Disposal Detection | |Radio Frequency Explosive Ordnance Disposal Detection | ||
| | | | ||
* EODD - | * EODD - uses an external handheld Metall Re-radiation Radar (MET3R) device, via a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi Direct connection | ||
|- | |- | ||
|RWR | |RWR | ||
|Radar Warning Receiver<ref name=":4">Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:List_of_radar_types|"List of radar types"]], [[wikipedia:Counter-battery_radar|"Counter-battery radar"]]</ref> | |Radar Warning Receiver<ref name=":4">Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:List_of_radar_types|"List of radar types"]], [[wikipedia:Counter-battery_radar|"Counter-battery radar"]]</ref> | ||
| | | | ||
* RWR - | * RWR - turns on the mode of detecting exposure from air defense radars and counter-battery radar<ref name=":5">Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:Counter-battery_radar|"Counter-battery radar"]]</ref>, displays on the screen in a window with a navigation grid and/or a map the geolocation of these radars | ||
* RWR mode is indispensable when performing tactical tasks of mortar and artillery fire | |||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="5" |[[File:Firing Assistance modes@4x.png|left|frameless|20x20px]] | | rowspan="5" |[[File:Firing Assistance modes@4x.png|left|frameless|20x20px]] | ||
| rowspan="5" |Firing assistance modes | | rowspan="5" |Firing assistance modes | ||
'' | ''OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset)'' | ||
|GF | |GF | ||
|Fire on ground fixed targets | |Fire on ground fixed targets | ||
| | | | ||
* | * captures and tracks up to 10 targets simultaneously | ||
* | * for each target calculates the ballistic trajectory at a distance based on 20 parameters | ||
* | * displays 16 ballistic calculation reference data (display can be turned off) | ||
* | * the user sees in the interface and can make manual changes (input field) to the parameters of the ballistic calculation | ||
* | * displays the aiming point taking into account corrections on the reticle relative to the crosshair with a scale in the form of digital data (Eunit and Wunit) MOA/MIL (true minute of angle/milliradian) | ||
* | * separately displays the numerical values of the corrections: Elevation and Windage when using Red Dot Sights or Holographic Sights (both eyes open), the user visually compares the position of the aiming dot and corrections relative to the crosshair on the screen (point of impact) and the contour of the target - with the contour in the sight window and the sight dot (usually 2-5 MOA), such shifting the sight dot (line of sight) in a way to hit the target at the crosshair point as on the screen of the device | ||
*when integrated with a digital sight, it immediately displays on the screen in the form of a diamond the sighting line of the digital sight, which must be aligned with the displayed aiming point | |||
* | *evaluates the inaccuracies of the ballistic calculation in case of a miss and offers the user corrections (takes into account aiming inaccuracies only for a digital sight) | ||
* | |||
|- | |- | ||
|GM | |GM | ||
|Fire on ground moving targets | |Fire on ground moving targets | ||
| | | | ||
* | * additionally calculates the angular velocity for the uniform movement of the target, the measurement of the distance to the target, the course of the target and indicates corrective lead corrections | ||
|- | |- | ||
|AM | |AM | ||
|Fire on aerial moving targets | |Fire on aerial moving targets | ||
| | | | ||
* | * additionally calculates the angular velocity, change in azimuth and elevation, determines the nearest probable trajectory with the designation of corrective lead corrections | ||
|- | |- | ||
|MF | |MF | ||
|Mountain fire on fixed targets (prospective function) | |Mountain fire on fixed targets (prospective function) | ||
| | | | ||
* | * additionally takes into account more complex parameters for calculating a ballistic trajectory in mountainous and desert areas based on an assessment of the landscape, temperatures, an assessment of ascending air currents and the mirage effect, shot history | ||
|- | |- | ||
|MM | |MM | ||
|Mountain fire on moving targets (prospective function) | |Mountain fire on moving targets (prospective function) | ||
| | | | ||
* | * as above plus additionally calculates angular velocity and denotes lead corrections | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="4" |[[File:Stealth modes@4x.png|left|frameless|27x27px]] | | rowspan="4" |[[File:Stealth modes@4x.png|left|frameless|27x27px]] | ||
| rowspan="4" |Stealth modes | | rowspan="4" |Stealth modes | ||
'' | ''OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset)'' | ||
|IFF | |IFF | ||
|IFF visible only | |IFF visible only | ||
| | | | ||
* | * all radio transmissions (including outgoing IFF interrogation signals) are blocked, with the exception of encrypted response messages of the Identification Friend-or-foe system transponder, including masking the transmission of a response message in the background noise frequency range of the broadcasting band (FM, TV) and using more long pauses in response intervals to interrogation signals (other radio strategies are possible to remain unnoticed) | ||
* | * this mode enables the IFF mode of the same name in the Radio Detection modes section, if it has not been enabled | ||
|- | |- | ||
|SD | |SD | ||
|Short distance visible only | |Short distance visible only | ||
| | | | ||
* | * only short range networks such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct (P2P) and UHF are used with limited transmission power over short distances | ||
|- | |- | ||
|FULL | |FULL | ||
|Zero emission | |Zero emission | ||
| | | | ||
* | * all radio transmissions are blocked, only reception (completely passive mode), IFF mode is automatically turned off (and vice versa, when changing Stealth mode to another, IFF mode is turned on again) | ||
* | * in full stealth mode, the user will not be able to turn on the flashlight and loudspeaker | ||
|- | |- | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| | | | ||
* | * does not restrict radio transmission | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="4" |[[File:Vitals Body tracking modes@4x.png|left|frameless|26x26px]] | | rowspan="4" |[[File:Vitals Body tracking modes@4x.png|left|frameless|26x26px]] | ||
| rowspan="4" |Vitals body tracking modes | | rowspan="4" |Vitals body tracking modes | ||
'' | ''OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset)'' | ||
|WRK | |WRK | ||
|Workout mode | |Workout mode | ||
| | | | ||
* Vitals body data-driven monitoring including: HR | * Vitals body data-driven monitoring including: HR bpm (ECG)<ref>Wikipedia, [[wikipedia:Monitoring_(medicine)|"Monitoring (medicine)"]]</ref> - assessment of rhythm and heart rate; NIBP mmHg (ART) - blood pressure; TEMP - body temperature; StO₂ % - non-invasive method for monitoring the level of oxygen saturation (saturation); ETCO₂ % - (capnometry) to measure the level of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) and methemoglobin (MetHb); RESP bpm (RR) - Respiratory Rate; HYDRL - determines the amount and frequency of hydration | ||
* | * displays tips for the user in case of many unwanted risks: bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, hypothermia, hyperthermia, hypoxemia, hyperventilation, hemorrhagic shock, etc. | ||
* | * when a dangerous level of indicators occurs, displays a message to the user and sends an SOS message to the analytical center | ||
* | * keeps a log of monitoring states | ||
|- | |- | ||
|TRN | |TRN | ||
|Training mode | |Training mode | ||
| | | | ||
* | * additionally takes into account the duration of the session of training exercises and the possibility of live fire training | ||
* | * applies a programmatically set training mode for the use of automatic tourniquets | ||
|- | |- | ||
|TACT | |TACT | ||
|Tactical mode | |Tactical mode | ||
| | | | ||
* | * in addition to the above, if a dangerous level of acute massive blood loss occurs in one of the 8 sites protected by automatic tourniquets, it controls the "Care Under Fire" task for stop of acute bleeding and start emergency automatic fluid resuscitation | ||
* | * if there is a risk of ventricular fibrillation, it automatically starts the defibrillation procedure under ECG control (cardio resuscitation) | ||
* | * if necessary, start automatic pulmonary resuscitation using pneumatic pumps built into the design of air filters | ||
|- | |- | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
|OFF | |OFF | ||
| | | | ||
* | * does not monitor | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="4" |[[File:Networks modes@4x.png|left|frameless|34x34px]] | | rowspan="4" |[[File:Networks modes@4x.png|left|frameless|34x34px]] | ||
| Line 729: | Line 737: | ||
|Network 1 | |Network 1 | ||
| | | | ||
* | * displays a scale with the bandwidth level of each connected network | ||
* | * displays the status of receiving and transmitting packets | ||
* | * displays the packet transmission prohibition | ||
* | * long click launches NET application | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 15 July 2023
Abstract
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:ARHUDFM Manifesto
→redirect Further information: Public:ARHUDFM Manifesto
Augmented Reality Heald-Up Display Fullface Mask (ARHUDFM) is a complex device that is not easy to understand at a first look, because there are little relevant examples to compare. Therefore, we suggest that you first read the information on the Public:ARHUDFM Manifesto page at the link above.
This page describes the structure and contents of the GUI (Graphical User Interface) used in the ARHUDFM device.
For a brief description of the functions of each application, please see the Public:Applications page.

Interface description
Appearance
| Left | Center | Right | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMP | Left main menu fading pads | SBP | Status bar fading pads | RSBP | Right submenu fading pads |
| LQMP | Left quick menu fading pads | CLW | Central left window | RQMP | Right quick menu fading pads |
| LFSP | Left features sidebar fading pads | CRW | Central right window | RFSP | Right features sidebar fading pads |
| LUW | Left Upper window | CWJP | Central window joystick pads | RUW | Right Upper window |
| LTAW | Left Top A window | CWBP | Central window buttons pads | RTAW | Right Top A window |
| LTBW | Left Top B window | RTBW | Right Top B window | ||
| LBAW | Left Bottom A window | RBAW | Right Bottom A window | ||
| LBBW | Left Bottom B window | RBBW | Right Bottom B window | ||
Features
The interface is designed for the screen of the ARHUDFM device with FOV 105°h (stereo overlap) and 33°v, has a resolution of 2560px in width.
Normal human stereoscopic binocular vision is 180° horizontally, up 55°, down 60°.[1] If the area of peripheral vision important for situational awareness is excluded, a comfortable field of view, especially if a person wears optic corrective glasses, will be 105-115° horizontally, 20° up and 25° down. Since the airway obturator of the mask from below is an obstacle to vision, the field of view of a person wearing a mask from below is less than usual (however, pilots of combat aircraft have sufficient visibility). Horizontally, the mask user has a complete view of the entire field of view, including the peripheral part, which is important.
The visible field is projected by the LED beams of a DLP projector offering high contrast and better color reproduction with high response.
Unlike the harmful effects of the blue light spectrum (light colors contain a lot of blue) emitted by the LED screen of a monitor or mobile device, which causes fatigue, headaches and sleep problems when exposed for a long time, the reflected light of a DLP projector (and other types of projectors also) does not have such disadvantages. In addition, in the ARHUDFM device, the principle of displaying the interface resembles the night mode (dark background, light graphic symbols). These conditions for the user create the possibility of round-the-clock work without stress.
The constant optical focus is set to an apparent distance of 1900 mm (75 in) from the user's eyes, which prevents conflict of vergence and accommodation so that the user's eyes do not get tired during long-term use. No virtual visual objects have a different image depth, just as if the user were to observe the display screen at a distance of 1900 mm while observing the rest of the environment with the focus oriented to infinity. This statement is based on numerous studies and experiments of different laboratories with a large number of respondents.
The tension of the muscles of the eye due to the close distance to the object in question causes fatigue, including being one of the causes of the development of myopia. Neck muscle tension and stoop due to the need to focus on a fixed part of field of view for a long time is also an unfavorable factor. This applies to all cases of human work with the screens of laptops, mobile devices, reading paper books and documents.
To imagine the actual visible edges (not the focal length) of the screen, sit in front of a 65" or 1440mm (57.3 inches x 32.9 inches) TV screen at a distance of 22" or 550mm from your eyes. You can clearly see the right and left sides of the screen by turning your eyes. You don't need to use the peripheral part of the vision at the edges, it remains completely open due to the wide field of view of the device's visor. Only in the lower part, when using the airway obturator of the device, the field of view of the user is limited to about 20°, as is the case with any respirator or when wearing most models of glasses. Glasses tend to shrink the effective field of view to somewhere between 90 and 115 degrees horizontally and 35-45 degrees vertically, depending on the width and hight of the glasses and their proximity to the eyes.
We've added these comments because most people don't have experience with these kinds of AR devices yet. Microsoft IVAS (Hololens 2) uses holographic optics, thick lenses and FOV 43°h 28°v, Magic Leap has similar technology to Microsoft and FOV 45°h 55°v. Apple Vision Pro is a VR device (opaque LED display) like the Meta (Oculus) Quest - FOV 90°h 98°v[2], HTC Vive, SONY Playstation, etc. None of these technologies or devices are like ARHUDFM and when used in tactical tasks carry many significant risks. More about it here.
The main feature of Augmented Reality devices is that a person can only see lighter areas on a darker screen background. The nature of vision is that a person sees not objects, but the light reflected from them. Those, can see a high-contrast image in a darkened room (Microsoft uses a tinted visor) or at night, but see almost nothing against a bright sky, on a sunny day, with strong reflections from snow or building walls, when looking at the sun. A person will not be able to see dark areas on a light background in principle, since this contradicts the physics of light (dark areas are the absence of light). The ARHUDFM solves this problem by using "smart windows" - the interface contains 10 large and 56 small fading pads that instantly change their transparency from 0% (opaque black) to 100% (fully transparent) depending on the ambient light or the mode selected by the user.
Principles
Since the user interface of the ARHUDFM device has more functions than is usually used by users of computers and mobile devices, and the device is such that it can be used for a long time in tactical conditions, the following principles are observed:
- As small screen area as possible should obstruct the view of the actual visual environment at all times
- The user must maintain the minimum necessary view of the visual environment for orientation in space
- If any element of the interface is not directly needed by the user at the moment, it should not be displayed on the screen
- The user should be able to change the interface configuration very quickly
- The user must be able to simultaneously clearly distinguish between interface elements and the visual environment at any brightness.
- Interface elements must not be visible from the outside of the device or create light emission to the outside
- The user's face must not be illuminated by reflected radiation, must not be visible from the outside at the night
- The audio environment should not have an attenuation greater than 10 dB SPL, except when using the noise reduction features
Interface controls
Right hand hardware controls
- Joystick. Cursor movement, drone and robot control
- Device on/off button
- Headphone mode control button (see Status bar)
- Button "- >". Decrease, right arrow, PgDown.
- Button "< +". Increase, left arrow, PgUp.
- Button C. Click, left control button
- Button D. Context menu, Shift, right control button
Left hand hardware controls
- Headlamp (Spotlight) on / off button
- Headset connector for handheld portable / manpack radio (also ground / vehicular radio headset cable)
- Loudspeaker on / off and control button
- Button "< -". Decrease, left arrow, PgDown
- Button "+ >". Increase, right arrow, PgUp
- Button A. Click, left control button, headset PTT button for radio
- Button B. Context menu, Shift, right control button, Photo, other assigned functions
- Buttons A+B simultaneously start / stop video record
Software controls
- Voice assistant
- Machine learning (AI) algorithms are used to recognize the meaning of user commands, not necessarily the exact pronunciation of the voice command, including the ability to adapt to the voice and pronunciation of the user
- Gesture control
- The stereo camera captures the image of the hands and recognizes the user's gestures (more details on the Hand Tracking page)
- Gesture library constantly updated, Machine Learning allows the user to create custom gestures
- Gestures can indicate not only the state, but also the dynamics, for example, smoothly change the volume level, brightness, etc.
- Capturing and recognizing fingers allows to use software interface controls, including scrollbars, buttons (and a virtual keyboard if necessary), swipe sideways and up or down, scale and rotate screens inside a window, hide and move windows
Perception hardware
The advantage of this wearable and inexpensive device for tactical use by almost every military person is the ability to perceive light, sound and radio waves, inaccessible to humans.
- Cameras
- Image capture with a three-sensor front stereo camera. One objective lens transmits the image to the separation prisms and then to 3 sensors: DSLR IR-cut 4K/8K/12K UHD, SenSWIR, HDR
- Separate camera in the range of LWIR (thermal image vision)
- Separate rear view camera with extended visible light and SWIR
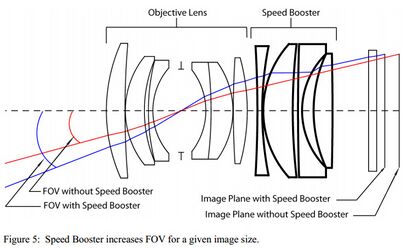
- Built-in Speed Booster reduces focal length and increases aperture for individual sensors
- Built-in teleconverter, on the contrary, increases the focal length for other sensors, increasing the image of distant objects
- Infrared and laser light sources are not used in this device, because this unmasks the user
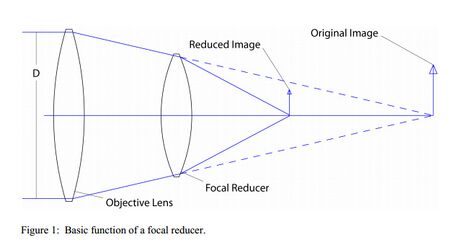
- Microphones
- Built-in MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) mask airway obturator to transmit the user's voice
- An omnidirectional microphone on the front side of the mask allows to perceive sound waves in a wide range of frequencies, including those inaudible to humans, from very low to very high (used in Computer Audition modes)
- 1 or 2 ultra-cardioid microphones with a narrow polar pattern on the front of the mask allows to accurately determine the source of the sound wave (used in Computer Audition modes)
- 2 insulating layers, airway obturator and seal around face make the user's voice almost inaudible from the outside
- Radio antennas
- Built-in transmit-receive antennas in the ranges of the near radius of communications (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE, 5G)
- Integrated manpack antennas for communications in the VHF, UHF, UHF SAT, MUOS, L/S bands
- Integrated manpack antennas for analyzing and listening to the frequency ranges 2 MHz - 6 GHz
- Not every user needs a separate antenna or a set of several antennas with different characteristics, using the P2P network within the group, packets of messages and received data can be exchanged and routed
- Integrated passive radar antenna with active phased array (installed in NVG mount)
- Integrated handheld portable short-range active metal re-radiation radar antenna
- Integrated receiving antenna for radar warning system
- Integrated antenna for remote control of a drone or robot
- Integrated antenna for close-range remote control of an active phased array radar (portable or vehicle-mounted)
- Software-defined (reconfigurable) antenna (installed in NVG mount and the other two via the picatinny rails on the sides of the helmet)
- The software-defined antenna is capable of combining the functions of most integrated antennas
The specific is that when using a separate optical lens for each sensor on the left and right, there is a problem of parasitic multi-angle, which will have to be constantly leveled by software, which affects the accuracy of binocular stereo vision. If in a smartphone this is not critical, and there may be 4-8 cameras with their own optics, then for tactical tasks this is of great difficulty. In this case, on the left and right, it is necessary to accurately hold the horizontal distance between the lines of sight for each pair of sensors and position them vertically, and then programmatically compensate for the vertical shift in order to reproduce a single optical axis for the left and right channels. In addition, the design of the device should allow this to be done without difficulty, including taking into account the angle of the field of view of the optics and solving the problem of shadowing.
Menu items description
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
→redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
The menu has 7 functional sections:
- Status bar (SB)
- Left main menu (LMM)
- Right submenu (RSB)
- Left quick menu (LQM)
- Right quick menu (RQM)
- Left features sidebar (LFS)
- Right features sidebar (RFS)
The principle of managing menu items of some sections is the same, and some are different.
Status bar (SB)
The status bar is located in the top middle of the visible area and contains all the main and frequently used information about the use of device functions and applications.
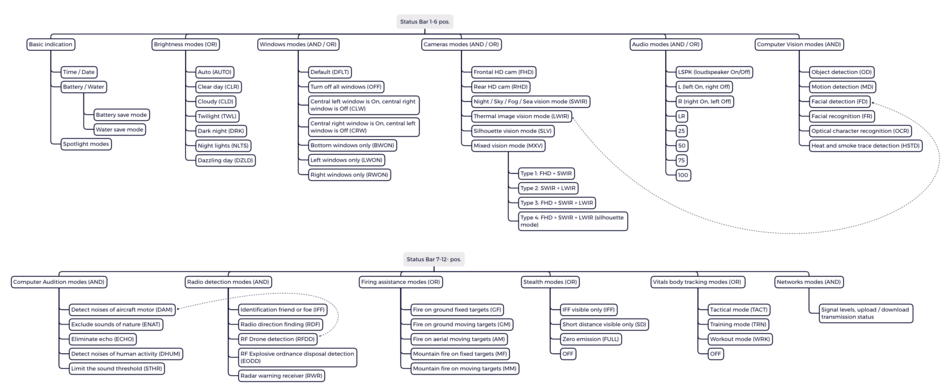
A total of 12 items for quick selection and tracking are available in the status bar, each of which contains sub-elements responsible for specific function presets. Preset settings are carried out not through the status bar, but in the settings of services or applications. The status bar is always displayed and is not hidden. Each element is located in a separate field (fading pad).

The sub-elements of the status bar are controlled by clicking (joystick, gesture control) or by voice (the result corresponds to the click). Default states:
- Hover state: 4 corner segments of the field frame (in the above example in the "Radio Detection modes" field with the "IFF" function)
- Click state: frame on the border of the field (animation effect, twice 100 ms), with each click sequenced display of list elements (presets)
- Selected (long click >2 s): vertically positioned rectangle in the lower left corner
- Not selected (long click >2 s): no vertical rectangle in the lower left corner
Differences in voice control:
- The command to the voice assistant contains a description of the desired action and state, so it is faster
- The voice assistant understands different interpretations of actions and states, so there is no need to memorize voice commands
SB indication and change of display
SB Presets
| Indication | Field name | Preset | Preset name | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time / Date, Battery, Water, Spotlights modes | na | Time / Date |
| |
| na | Battery |
| ||
| na | Water |
| ||
| na | Spotlight |
| ||
| Brightness modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
AUTO | Auto |
| |
| CLR | Clear day | fading pads 50%, fading windows 50%, projector beam 100% | ||
| CLD | Cloudy | fading pads 25%, fading windows 25%, projector beam 75% | ||
| TWL | Twilight | fading pads 0%, fading windows 0%, projector beam 75% | ||
| DRK | Dark night | fading pads 0%, fading windows 0%, projector beam 50% | ||
| NLTS | Night lights | fading pads 50%, fading windows 25%, projector beam 75% | ||
| DZLD | Dazzling day | fading pads 75%, fading windows 75%, projector beam 100% | ||
| Windows modes
AND / OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case cancels, and in the other case does not cancel the selection of the previously selected preset) |
DFLT | Default | displays all active windows according to the configured application and feature priorities; DFLT - deselects any previously selected preset | |
| OFF | Turn off all windows | turns off the display of all windows; OFF - deselects any previously selected preset | ||
| CLW | Central left window is On, central right window is Off | if both central windows (left and right) were used by default, disables the central right window, all functions remain available in the central left window; CLW cancels CRW and vice versa | ||
| CRW | Central right window is On, central left window is Off | as in the previous case, on the contrary, disables the central left window, improving the view of the environment; CRW cancels CLW and vice versa | ||
| BWON | Bottom windows only | turns off the upper windows (except LUW and RUW) on the left and right to improve the view ("knight's narrow visor effect"), transfers higher priority windows to the lower area, closes lower priority windows, does not turn off the central windows; BWON cancels LWON and RWON | ||
| LWON | Left windows only | turns off all windows on the right (except RUW) ("left eye effect"), transfers higher priority windows to the left area, closes lower priority windows, does not turn off central windows; LWON cancels RWON and BWON | ||
| RWON | Right windows only | turns off all windows on the left (except LUW) ("right eye effect"), transfers higher priority windows to the right area, closes lower priority windows, does not turn off central windows; RWON cancels LWON and BWON | ||
| Cameras modes
AND / OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case cancels, and in the other case does not cancel the selection of the previously selected preset) |
FHD | Frontal HD cam | uses visible light range (400-780 nm) and dual sensor capabilities, high resolution and wide dynamic range under strong contrast lighting | |
| RHD | Rear HD cam | turn the rear view camera on and off | ||
| SWIR | Night / Sky / Fog / Sea vision mode | uses a wider short-wavelength infrared light range (780-1700 nm), which is used to observe the reflection of ambient light in this range by objects located on the surface of the water, in fog, in smoke, in clouds, at dusk and at night | ||
| LWIR | Thermal image vision mode | uses long-wavelength invisible infrared light (7.5-14 µm) emitted by objects warmer in relation to the environment, mainly at night | ||
| SLV | Silhouette vision mode | turns on the transformation of the fill into a color outline mode that is well distinguishable in relation to the background for contrasting objects | ||
| MXV1 | Mixed vision mode Type 1: FHD + SWIR | allows to use the capabilities of three different sensors in different conditions day and night; 4K UHD + HDR + SWIR | ||
| MXV2 | MXV Type 2: SWIR + LWIR | allows to use the capabilities of two different sensors in different conditions day and night; SWIR + LWIR | ||
| MXV3 | MXV Type 3: FHD + SWIR + LWIR | allows to use the capabilities of four different sensors in different conditions day and night; 4K UHD + HDR + SWIR + LWIR | ||
| MXV4 | MXV Type 4: FHD + SWIR + LWIR (silhouette mode) | allows to use the capabilities of four different sensors in different conditions day and night; 4K UHD + HDR + SWIR + LWIR (silhouette mode) | ||
| Audio modes
AND / OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case cancels, and in the other case does not cancel the selection of the previously selected preset) |
LSPK | Loudspeaker On/Off |
| |
| L | Left On, right Off |
| ||
| R | Right On, left Off |
| ||
| LR | Left On, right On |
| ||
| 25 | 25% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 25 cancels 50, 75, 100 | ||
| 50 | 50% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 50 cancels 25, 75, 100 | ||
| 75 | 75% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 75 cancels 25, 50, 100 | ||
| 100 | 100% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 100 cancels 25, 50, 75 | ||
| Computer Vision[3][4] modes
AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset) |
OD | Object detection |
| |
| MD | Motion detection |
| ||
| FD | Facial detection |
| ||
| FR | Facial recognition |
| ||
| OCR | Optical character recognition |
| ||
| HSTD | Heat and smoke trace detection |
| ||
| Computer Audition modes
AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset) |
DAM | Detect noises of aircraft motor |
| |
| ENAT | Exclude sounds of nature |
| ||
| ECHO | Eliminate echo |
| ||
| DHUM | Detect noises of human activity |
| ||
| STHR | Limit sound threshold |
| ||
| Radio detection modes
AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset) |
IFF | Identification Friend-or-Foe |
| |
| RDF | Radio Direction Finding[6] |
| ||
| RFDD | Radio Frequency Drone Detection[7] |
| ||
| EODD | Radio Frequency Explosive Ordnance Disposal Detection |
| ||
| RWR | Radar Warning Receiver[8] |
| ||
| Firing assistance modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
GF | Fire on ground fixed targets |
| |
| GM | Fire on ground moving targets |
| ||
| AM | Fire on aerial moving targets |
| ||
| MF | Mountain fire on fixed targets (prospective function) |
| ||
| MM | Mountain fire on moving targets (prospective function) |
| ||
| Stealth modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
IFF | IFF visible only |
| |
| SD | Short distance visible only |
| ||
| FULL | Zero emission |
| ||
| OFF | OFF |
| ||
| Vitals body tracking modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
WRK | Workout mode |
| |
| TRN | Training mode |
| ||
| TACT | Tactical mode |
| ||
| OFF | OFF |
| ||
| Networks modes
AND |
Network 1 |
| ||
| Network 2 | ||||
| Network 3 | ||||
| Network 4 | Signal levels, upload / download transmission status |
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
→redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
| Left | Center | Right | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMP | Left main menu fading pads | SBP | Status bar fading pads | RSBP | Right submenu fading pads |
| LQMP | Left quick menu fading pads | CLW | Central left window | RQMP | Right quick menu fading pads |
| LFSP | Left features sidebar fading pads | CRW | Central right window | RFSP | Right features sidebar fading pads |
| LUW | Left Upper window | CWJP | Central window joystick pads | RUW | Right Upper window |
| LTAW | Left Top A window | CWBP | Central window buttons pads | RTAW | Right Top A window |
| LTBW | Left Top B window | RTBW | Right Top B window | ||
| LBAW | Left Bottom A window | RBAW | Right Bottom A window | ||
| LBBW | Left Bottom B window | RBBW | Right Bottom B window | ||
Главное меню (LMM) находится слева сверху видимой области и содержит список разделов.
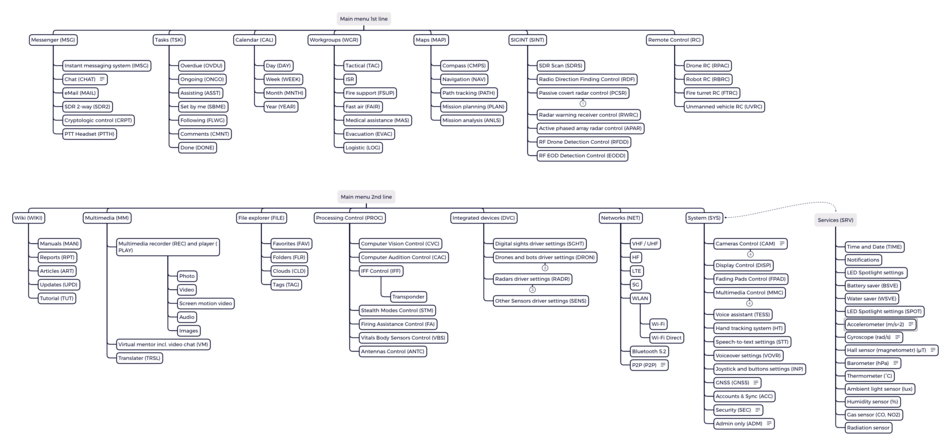
Всего 7 элементов для быстрого выбора в одном ряду. Для выбора следующего ряда используются навигационные стрелки справа. Главное меню отображается только при наведении курсора или при голосовом вызове. При неактивности скрывается через 15 сек. Каждый элемент расположен в отдельном поле (fading pad). Показываются только поля, отображающие раздел.
Правое субменю (RSB) находится сверху справа и раскрывает второй более низкий уровень элементов главного меню. Всего 7 элементов в одном ряду. Для навигации используются стрелки слева. Правое субменю отображается только при активном состоянии одного из пунктов главного меню слева (LMM) или при голосовом вызове непосредственно пункта субменю. При неактивности скрывается одновременно с главным меню через 15 сек. Каждый элемент расположен в отдельном поле (fading pad). Показываются только поля, отображающие раздел.
Когда приложение открыто с помощью данного меню, оно показывается на экране. Если пользователь закрывает приложение, оно не прекращает свою работу, а продолжает работать в фоновом режиме, одновременно в поле меню LQM (right quick menu) или RQM (right quick menu) появляется элемент с названием данного приложения для быстрого возврата на экран. Как полностью прекратить работу приложения, см. ниже в разделах Left quick menu (LQM) и Right quick menu (RQM).
(!) Картинки с внешним крупным видом LMM и отдельно крупно RSB вставить здесь:
Управление субэлементами главного меню и субменю выполняется кликом (джойстик, управление жестами) или голосом. Состояния:
- Hover state: 4 угловых сегмента рамки поля
- Click state: рамка по границе поля (эффект анимации, дважды по 100 ms)
- Selected (long click >2 s): горизонтально расположенные два прямоугольника справа и слева от надписи
- Not selected (long click >2 s): горизонтально расположенные два прямоугольника справа и слева от надписи отсутствуют
Отличия при голосовом управлении:
- Команда голосовому ассистенту содержит описание требуемого действия и состояния, поэтому выполняется быстрее
- Голосовой ассистент понимает разные интерпретации действий и состояний, поэтому не нужно запоминать голосовые команды наизусть
- При голосовом вызове показывается не всё меню целиком, а соответствующие пункты главного меню и субменю
- Пользователь может вызвать голосом отображение всего меню целиком
| LMM | RSB | Action | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSG
(Messenger) |
IMSG (instant messaging system) |
|
|
| CHAT (multichannel chat) |
|
LMM для всех каналов, RSB и RFS для соответствующего канала:
| |
| MAIL (eMail) |
|
||
| SDR2 (SDR 2-way) |
|
||
| CRPT (cryptologic control) |
|
||
| PTTH (PTT headset) |
|
||
| TSK (Tasks) |
|
Система управления задачами позволяет планировать и контролировать срок, точность, результаты, эффективность выполнения задач. Содержит описание, чек-лист, дедлайн, фактическое время выполнения и затраченное время (в т.ч. автотрекинг завершения и отсчёт затраченного времени), уведомление о текущем статусе, геопозицию в момент завершения, артефакты подтверждения выполнения задачи, вложения, комментарии |
|
| CAL (Calendar) |
|
Календарь событий позволяет заранее планировать и согласовывать события, требующие определённого регламентов времени: коллективные онлайн и офлайн коммуникации, собрания, учебные семинары, командировки |
|
| WGR (Workgroups) |
|
Субменю содержит фильтры для групп.
Можно выбрать участника или группу в соответствующем разделе для коммуникаций, обмена данными, отправки или запроса позиции. Элемент CDI (Cross-Domain Interaction) |
|
| MAP
(Maps & Navigation) |
CMPS (Compass) |
|
|
| NAV (Navigation) |
|
||
| PATH (Path tracking) |
|
||
| PLAN (Mission planning) |
|
| |
| ANLS (Mission analysis) |
|
| |
| SINT
(SIGINT) |
SDRS (SDR Scan) |
|
|
| RDF (Radio Direction Finding Control) |
|
||
| PCSR (Passive covert radar control) |
|
||
| RWRC (Radar warning receiver control) |
|
||
| APAR (Active phased array radar control) |
|
||
| RFDD (RF Drone Detection Control) |
|
||
| EODD (RF EOD Detection Control) |
|
||
| RC
(Remote Control) |
RPAC (Drone RC) |
|
|
| RBRC (Robot RC) |
|
||
| FTRC (Fire turret RC) |
|
||
| UVRC (Unmanned vehicle RC) |
|
||
| WIKI (Wiki) |
|
Вики-системы доказатели свою эффективность для накопления и обмена знаниями, которые необходимы каждому почти ежедневно. Данная система позволяет собирать лучшие практики и улучшать процесс обучения и тренировки, а также время от времени освежать знания даже у опытных пользователей. Всевозможная информация о техническом устройстве и обслуживании оборудования, организации процессов на военных базах, расписания, материалы анализа военных экспертов и т.д. То, что поможет стать эффективнее. Безусловно, распределённые права доступа, защита информации и конфиденциальность в соответствии с действующими протоколами. |
|
| MMD (Multimedia) | REC (multimedia recorder)
PLAY (multimedia player) |
|
|
| VM (Virtual mentor incl. video chat) |
|
||
| TRSL (Translater) |
|
||
| FILE (File explorer) |
|
|
|
| PROC (Processing Control) | CVC (Computer Vision Control) |
|
|
| CAC (Computer Audition Control) |
|
||
| IFF (IFF Control) |
|
||
| STM (Stealth Modes Control) |
|
||
| FA (Firing Assistance Control) |
|
||
| VBS (Vitals Body Sensors Control) |
|
||
| ANTC (Antennas Control) |
|
||
| DVC (Integrated devices) |
|
|
|
| NET (Networks) |
|
|
|
| SYS (System) | CAM (Cameras Control) |
|
|
| DISP (Display Control) |
|
||
| FPAD (Fading Pads Control) |
|
||
| MMC (Multimedia Control) |
|
||
| TESS (Voice assistant) |
|
||
| HT (Hand tracking system) |
|
||
| STT (Speech-to-text settings) |
|
||
| VOVR (Voiceover settings) |
|
||
| INP (Joystick and buttons settings) |
|
||
| GNSS (GNSS) |
|
||
| ACC (Accounts & Sync) |
|
||
| SEC (Security) |
|
||
| ADM (Admin only) |
|
||
| SRV (Services) |
|
Отображает свёрнутые (внутри рамки) и открытые окна приложений левой половины экрана. Чтобы полностью прекратить работу приложения необходимо выполнить долгий клик и нажать подтверждение в окне нотификаций.
Отображает свёрнутые (внутри рамки) и открытые окна приложений правой половины экрана. Чтобы полностью прекратить работу приложения необходимо выполнить долгий клик и нажать подтверждение в окне нотификаций.
Left features sidebar (LFS)
Отображает:
- функциональные кнопки некоторых активных приложений в левой половине экрана, когда их много и нежелательно уменьшать видимую область окна приложения
- список приоритетных задач для приложения TSK
- список последних просмотренных статей для приложения WIKI
- список лидов в одноранговой сети для приложения P2P и их характеристики в реальном времени
- список приоритетных каналов для приложения WGR
Right features sidebar (RFS)
Отображает:
- функциональные кнопки некоторых активных приложений в правой половине экрана, когда их много и нежелательно уменьшать видимую область окна приложения (например, SDRS)
- список диалогов приложения CHAT и фильтры диалогов
- список последних команд через приложение IMSG
- список сделанных фотографий и видеозаписей для приложения PLAY
- список участников видеоконференции для приложения VM
Virtual control tools
Отображает:
- Программные (продублированные с аппаратными) джойстики и кнопки для управления дроном, роботом, турелью, беспилотным транспортом
- Программные кнопки управления камерами дронов, роботов и беспилотного транспорта
- Джойстики и кнопки для управления перемещением позиций на карте и отметки точек маршрута
- Кнопки управления и навигации для мультимедиа
Windows items description
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:Applications
→redirect Further information: Public:Applications
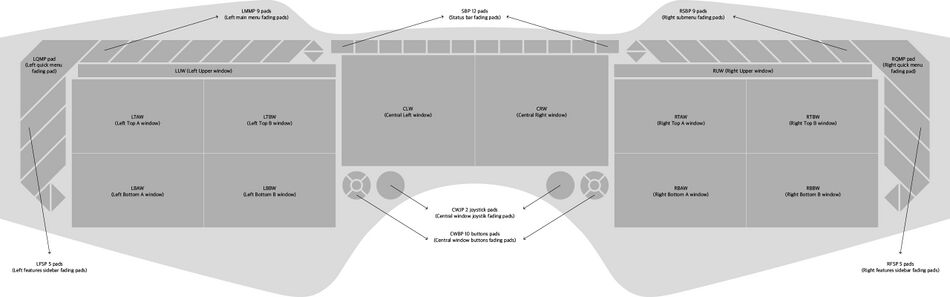
Fading windows and pads
| Left | Center | Right | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMP | Left main menu fading pads | SBP | Status bar fading pads | RSBP | Right submenu fading pads |
| LQMP | Left quick menu fading pads | CLW | Central left window | RQMP | Right quick menu fading pads |
| LFSP | Left features sidebar fading pads | CRW | Central right window | RFSP | Right features sidebar fading pads |
| LUW | Left Upper window | CWJP | Central window joystick pads | RUW | Right Upper window |
| LTAW | Left Top A window | CWBP | Central window buttons pads | RTAW | Right Top A window |
| LTBW | Left Top B window | RTBW | Right Top B window | ||
| LBAW | Left Bottom A window | RBAW | Right Bottom A window | ||
| LBBW | Left Bottom B window | RBBW | Right Bottom B window | ||
Как уже было написано в самом начале описания пользовательского интерфейса, в устройстве для контрастного отображения используются затухающие окна и площадки. Иначе на светлом и ярком фоне окружающей среды пользователю будет сложно видеть изображения контрастным. Затухающие окна и площадки в зависимости от режимов яркости имеют разную степень прозрачности. А в случае яркого света дополнительно выполняют функцию солнцезащитного экрана.
Окна приложений и функций располагаются в большей и наилучшей видимой области. Всего 12 независимых окон (8 больших 1.78:1, 2 больших 1.20:1, 2 малых 19.86:1), каждое из которых содержит субэлементы управления, когда окно выделено с помощью клика или голосом (selected state). Не выделенное окно является пассивным окном, которое отображает только графику приложения, элементы управления окном скрыты, элементы управления приложением скрыты. Окна разных прилоожений имеют разный приоритет отображения, который настраивается в настройках системы для каждого приложения. В зависимости от выбранного пресета в Status bar (SB) конфигурации отображаемых окон могут быть быстро и гибко изменены пользователем.
(!) Вставить галерею с картинками примеров
Управление субэлементами окон выполняется кликом (джойстик, управление жестами) или голосом. Состояния:
- Hover state: частая пунктирная линия вдоль рамки поля
- Click state: рамка по границе поля (эффект анимации, дважды по 100 ms)
- Selected (long click >2 s): редкая пунктирная линия вдоль рамки поля
- Not selected (long click >2 s): пунктирная линия отсутствует
Отличия при голосовом управлении:
- Команда голосовому ассистенту содержит описание требуемого действия и состояния, поэтому выполняется быстрее
- Голосовой ассистент понимает разные интерпретации действий и состояний, поэтому не нужно запоминать голосовые команды наизусть
Пользователь может быстро и гибко управлять конфигурацией окон для каждого окна в отдельности:
- Пользователь может принудительно закрыть любое окно в любое время, выделив нужное окно (selected state), нажав на иконку "закрыть окно" (приложение остаётся в фоновом режиме, для обратного действия кликнуть на иконку в меню быстрого выбора)
- Пользователь может увеличить левое или правое большое центральное окно на всю область центрального окна (объединённое окно 2.40:1), выделив нужное окно (selected state), нажав на иконку "увеличить окно"
- Пользователь может увеличить большое осно слева или справа на всю левую или правую область окна (объединённое окно 1.78:1 x2), выделив нужное окно (selected state), нажав на иконку "увеличить окно"
- При нажатии на иконку "уменьшить окно" окно возвращается в исходное состояние
- Иконка "сместить окно влево" смещает его влево, затем вверх направо, затем влево, меняя расположение других окон
- Иконка "сместить окно вправо" смещает окно вправо, затем вниз налево, затем вправо, меняя расположение других окон
- Иконка "поделиться экраном" позволяет отправить скриншот окна или включить трансляцию данного окна для другого пользователя
Apps priority for windows
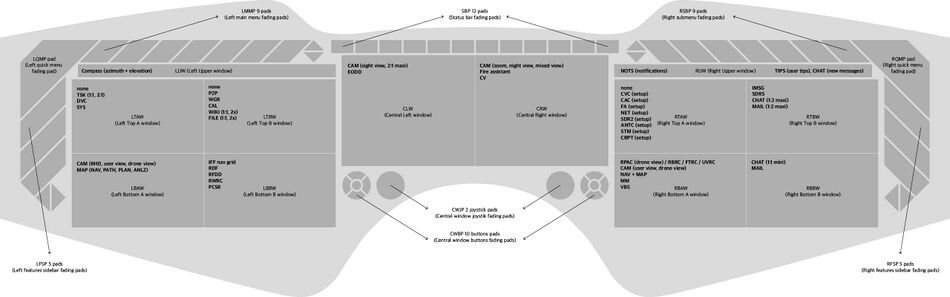
| LUW | CLW | CRW | RUW | ||
|
|
|
| ||
| LTAW | LTBW | CWJP (left) | CWJP (right) | RTAW | RTBW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LBAW | LBBW | CWBP (left) | CWBP (right) | RBAW | RBBW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Window | Mode | Notice |
|---|---|---|
| Left Upper window (LUW) | Обычно используется долговременно | |
| Left top A window (LTAW) | Используется при необходимости, не рекомендуется во время интенсивного боя, чтобы не ограничивать видимость окружающей среды | |
| Left top B window (LTBW) | Обычно используется кратковременно, чтобы не ограничивать видимость окружающей среды | |
| Left bottom A window (LBAW) | Обычно используется долговременно | |
| Left bottom B window (LBBW) | Обычно используется долговременно | |
| Central left window (CLW) | Обычно используется кратковременно, чтобы не ограничивать видимость окружающей среды | |
| Central right window (CRW) | Обычно используется долговременно | |
| Right Upper window (RUW) | Обычно используется долговременно | |
| Right top A window (RTAW) | Обычно используется кратковременно, чтобы не ограничивать видимость окружающей среды | |
| Right top B window (RTBW) | Используется при необходимости, не рекомендуется во время интенсивного боя, чтобы не ограничивать видимость окружающей среды | |
| Right bottom A window (RBAW) | Обычно используется долговременно | |
| Right bottom B window (RBBW) | Обычно используется долговременно |
Shifts windows to the left and right
- Общее правило "слева направо, сверху вниз" (список перемещения 10 больших окон):
- LTAW - left top window A
- LTBW - left top window B
- LBAW - left bottom window A
- LBBW - left bottom window B
- CLW - central left window
- CRW - central right window
- RTAW - left top window A
- RTBW - left top window B
- RBAW - left bottom window A
- RBBW - left bottom window B
- Если активное окно расположено в левой части и он перемещается влево, он перемещается выше по списку
- Если активное окно расположено в левой части и он перемещается вправо, он перемещается ниже по списку, сначала в центр видимой области, затем в правую часть
- Если место, куда перемещается активное окно не занято другим окном, другие окна не меняют своего положения
- Другой отображаемое окно, на место которого смещается активное окно вниз по списку, автоматически перемещается выше по списку и занимает предыдущее место смещаемого активного окна
- Другой отображаемое окно, на место которого смещается активное окно вверх по списку, автоматически перемещается ниже по списку и занимает предыдущее место смещаемого активного окна
- Обычно отображаются менее 10 больших окон, поэтому смещение активного окна не приводит с смещению большинства других окон
- Если отображаются все 10 больших окон, смещение активного окна на несколько позиций в списке вызывает последовательное автоматическое временное смещение соседнего окна, который затем снова возвращается на предыдущее место
- Если окно максимизировано, оно автоматически минимизируется и перемещается по общему правилу, при необходимости его нужно максимизирован снова
- Пользователь может выделить два или более окон одновременно, удерживая клавишу D (рядом с джойстиком) headphones ear cup правого наушника (аналогично правой клавиши мыши)
- Выделив окно и удерживая клавишу C (аналогично левой клавиши мыши) headphones ear cup правого наушника пользователь может переместить окно или несколько окон одновременно одним действием с помощью джойстика - в этом случае, если перемещается группа окон, они будут располагаться последовательно рядом по списку (даже если в предыдущем их местоложении они не были расположены последовательно рядом по списку)
- Малые окна перемещаются только влево или вправо на место аналогичного малого окна
- Если малое окно перемещается вправо, другое окно перемещается влево (меняются местами)
- Если приложение запускает малое окно в то время, когда оба малых окна отображают информацию других приложений, тогда окно с приложением, имеющим наименьший приоритет, скрывается в меню быстрого выбора
- Если одно малое окно закрывается, на его месте ничего не отображается, для отображения на этом месте окна другого приложения необходимо кликнуть на него в меню быстрого выбора или в главном меню
- Если приложение запускает большое окно, которое имеет больший приоритет для уже занятого окна, тогда окно с меньшим приоритетом перемещается в другое место, как предусмотрено правилами приоритета окон и приложений. При закрытии окна с большим приоритетом, конфигурация окон возвращается в предыдущее состояние
- Если приложение запускает большое окно, когда нет свободного места для отображения окон, окно с наименьшим приоритетом скрывается автоматически в меню быстрого выбора. При закрытии одного из окон с большим приоритетом, восстанавливается предыдущее состояние отображения окон. При необходимости отображения окна с меньшим приоритетом, необходимо освободить место для него, свернув один из окон в меню быстрого выбора
Прокрутка окна на (4/5 высоты окна или в строках - настраивается индивидуально) выполняется иконками вверх и вниз или кнопками джойстика "< +" и "- >" снизу headphones ear cup правого или левого наушника (аналогично клавишам мыши PageUp, PageDown). Также плавная прокрутка окна джойстиком, голосовой командой или жестом (в т.ч. виртуальным джойстиком или обособленным жестом).
Элементы управления (иконки управления окном, функциональные программные кнопки интерфейса приложения, расположенные на Sidebar Left or Sidebar Right, виртуальные джойстики) относятся только к активному (selected) окну. Для пассивного окна (not selected) они не отображаются.
Отдельно для иконок управления окном - после того, как окно стало активным (selected), иконки управления окном отображаются в течение 15 с, после чего исчезают. Для их повторного отображение необходимо снова выделить данное окно. Пунктирная рамка выделения активного окна отображается в течение всего времени активного состояния окна.
! Кроме того, принудительное использование некоторых окон может выполнить функцию солнцезащитного козырька тогда, когда солнце находится низко над горизонтом на линии визирования. Пользователь может смещать окно в нужную область и перекрывать ослепляющий вид на солнце, не затемняя всю область визирования.
Interface Animation
Interface Items Motion
- принципиальный вид
- активный вид при работе с меню
- процесс выбора пункта меню (скролл элементов, изменение вида при входе в подменю 1-го уровня / 2-го уровня / 3-го уровня)
- постоянный (продолжительный) вид (статусы, нотификации, активные пункты меню)
- включение и смена затухающих окон (правила, варианты комбинации в одновременном виде)
Modern tools
1. MRTK-Unity is a Microsoft-driven project that provides a set of components and features, used to accelerate cross-platform MR app development in Unity. Here are some of its functions:
- Provides the cross-platform input system and building blocks for spatial interactions and UI.
- Enables rapid prototyping via in-editor simulation that allows you to see changes immediately.
- Operates as an extensible framework that provides developers the ability to swap out core components.
- Supports a wide range of platforms.
2. Unity Mars helps solve the hard problems of AR app creation:
- Overcome the challenges of authoring for dynamic physical environments
- Reduce development time
- Release cross-platform experiences with support for iOS, Android, and HoloLens
Manuals
Troubleshooting
Areas of research
Related fields
Future ideas
Further reading
See also
| Public External Sections: | Public Wiki Sections: | Public Wiki Sections: | Not-Public Wiki Sections: |
|---|---|---|---|
Note: Unless otherwise stated, whenever the masculine gender is used, both men and women are included.
See also product details
| Hardware Details: | Functional Apps Details: | Executive Apps Details: | Service Apps Details: |
|---|---|---|---|
References
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Field of view"
- ↑ GitHub, Pimax Forum, "HMD Geometry Database"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Outline Computer Vision"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Computer Vision"
- ↑ Wikipedia, Artillery sound ranging
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Radio direction finding"
- ↑ AARTOS, "RF Drone Detection", "Antennas"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "List of radar types", "Counter-battery radar"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Counter-battery radar"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Monitoring (medicine)"