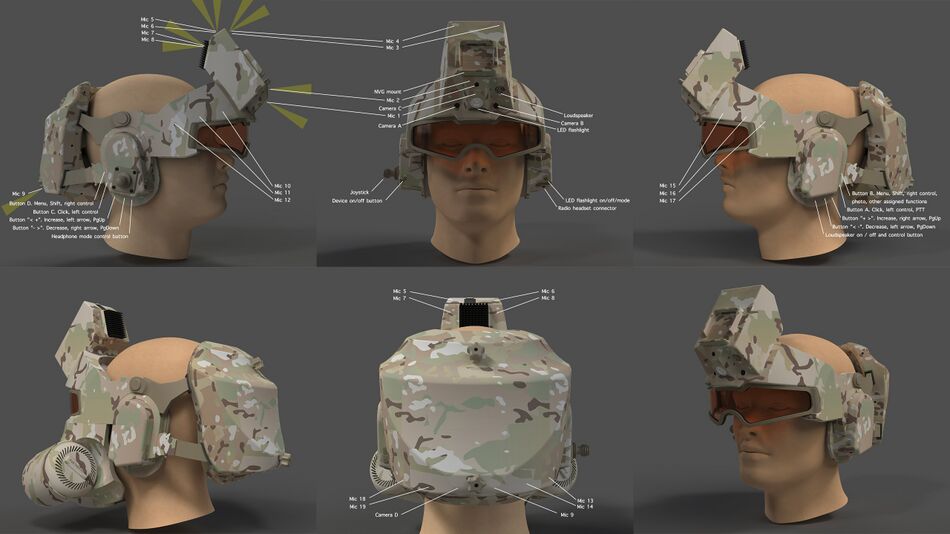
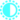Public:Graphical User Interface
Abstract
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:ARHUDFM Manifesto, Public:Applications, Public:ARHUDFM Features Summary
→redirect Further information: Public:ARHUDFM Manifesto, Public:Applications, Public:ARHUDFM Features Summary
Augmented Reality Heald-Up Display Fullface Mask (ARHUDFM) is a complex device that is not easy to understand at a first look, because there are little relevant examples to compare. Therefore, we suggest that you first read the information on the Public:ARHUDFM Manifesto page at the link above.
This page describes the structure and contents of the GUI (Graphical User Interface) used in the ARHUDFM device.
For a brief description of the functions of each application, please see the Public:Applications page.
Click on the picture to zoom in
Interface description
Appearance
| Left | Center | Right | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMP | Left main menu fading pads | SBP | Status bar fading pads | RSBP | Right submenu fading pads |
| LQMP | Left quick menu fading pads | CLW | Central left window | RQMP | Right quick menu fading pads |
| LFSP | Left features sidebar fading pads | CRW | Central right window | RFSP | Right features sidebar fading pads |
| LUW | Left Upper window | CWJP | Central window joystick pads | RUW | Right Upper window |
| LTAW | Left Top A window | CWBP | Central window buttons pads | RTAW | Right Top A window |
| LTBW | Left Top B window | RTBW | Right Top B window | ||
| LBAW | Left Bottom A window | RBAW | Right Bottom A window | ||
| LBBW | Left Bottom B window | RBBW | Right Bottom B window | ||
Features
The interface is designed for the screen of the ARHUDFM device with FOV 105°h (stereo overlap) and 33°v, has a resolution of 3840px in width and 1200 px in hight.
Normal human stereoscopic binocular vision is 180° horizontally, up 55°, down 60°.[1] If the area of peripheral vision important for situational awareness is excluded, a comfortable field of view, especially if a person wears optic corrective glasses, will be 105-115° horizontally, 20° up and 25° down. Since the airway obturator of the mask from below is an obstacle to vision, the field of view of a person wearing a mask from below is less than usual (however, pilots of combat aircraft have sufficient visibility). Horizontally, the mask user has a complete view of the entire field of view, including the peripheral part, which is important.
The visible field is projected by the LED beams of a DLP projector offering high contrast and better color reproduction with high response.
Unlike the harmful effects of the blue light spectrum (light colors contain a lot of blue) emitted by the LED screen of a monitor or mobile device, which causes fatigue, headaches and sleep problems when exposed for a long time, the reflected light of a DLP projector (and other types of projectors also) does not have such disadvantages. In addition, in the ARHUDFM device, the principle of displaying the interface resembles the night mode (dark background, light graphic symbols). These conditions for the user create the possibility of round-the-clock work without stress.
The constant optical focus is set to an apparent distance of 1900 mm (75 in) from the user's eyes, which prevents conflict of vergence and accommodation so that the user's eyes do not get tired during long-term use. No virtual visual objects have a different image depth, just as if the user were to observe the display screen at a distance of 1900 mm while observing the rest of the environment with the focus oriented to infinity. This statement is based on numerous studies and experiments of different laboratories with a large number of respondents.
The tension of the muscles of the eye due to the close distance to the object in question causes fatigue, including being one of the causes of the development of myopia. Neck muscle tension and stoop due to the need to focus on a fixed part of field of view for a long time is also an unfavorable factor. This applies to all cases of human work with the screens of laptops, mobile devices, reading paper books and documents.
To imagine the actual visible edges (not the focal length) of the screen, sit in front of a 65" or 1440mm (57.3 inches x 32.9 inches) TV screen at a distance of 22" or 550mm from your eyes. You can clearly see the right and left sides of the screen by turning your eyes. You don't need to use the peripheral part of the vision at the edges, it remains completely open due to the wide field of view of the device's visor. Only in the lower part, when using the airway obturator of the device, the field of view of the user is limited to about 20°, as is the case with any respirator or when wearing most models of glasses. Glasses tend to shrink the effective field of view to somewhere between 90 and 115 degrees horizontally and 35-45 degrees vertically, depending on the width and hight of the glasses and their proximity to the eyes.
We've added these comments because most people don't have experience with these kinds of AR devices yet. Microsoft IVAS (Hololens 2) uses holographic optics, thick lenses and FOV 43°h 28°v, Magic Leap has similar technology to Microsoft and FOV 45°h 55°v. Apple Vision Pro is a VR device (opaque LED display) like the Meta (Oculus) Quest - FOV 90°h 98°v[2], HTC Vive, SONY Playstation, etc. None of these technologies or devices are like ARHUDFM and when used in tactical tasks carry many significant risks. More about it here.
The main feature of Augmented Reality devices is that a person can only see lighter areas on a darker screen background. The nature of vision is that a person sees not objects, but the light reflected from them. Those, can see a high-contrast image in a darkened room (Microsoft uses a tinted visor) or at night, but see almost nothing against a bright sky, on a sunny day, with strong reflections from snow or building walls, when looking at the sun. A person will not be able to see dark areas on a light background in principle, since this contradicts the physics of light (dark areas are the absence of light). The ARHUDFM solves this problem by using "smart windows" - the interface contains 10 large and 56 small fading pads that instantly change their transparency from 0% (opaque black) to 100% (fully transparent) depending on the ambient light or the mode selected by the user.
Principles
Since the user interface of the ARHUDFM device has more functions than is usually used by users of computers and mobile devices, and the device is such that it can be used for a long time in tactical conditions, the following principles are observed:
- As small screen area as possible should obstruct the view of the actual visual environment at all times
- The user must maintain the minimum necessary view of the visual environment for orientation in space
- If any element of the interface is not directly needed by the user at the moment, it should not be displayed on the screen
- The user should be able to change the interface configuration very quickly
- The user must be able to simultaneously clearly distinguish between interface elements and the visual environment at any brightness.
- Interface elements must not be visible from the outside of the device or create light emission to the outside
- The user's face must not be illuminated by reflected radiation, must not be visible from the outside at the night
- The audio environment should not have an attenuation greater than 10 dB SPL, except when using the noise reduction features
Interface controls
Right hand hardware controls
- Joystick. Cursor movement, drone and robot control
- Device on/off button
- Headphone mode control button (see Status bar)
- Button "- >". Decrease, right arrow, PgDown.
- Button "< +". Increase, left arrow, PgUp.
- Button C. Click, left control button
- Button D. Context menu, Shift, right control button
Left hand hardware controls
- Headlamp (Spotlight) on / off button
- Headset connector for handheld portable / manpack radio (also ground / vehicular radio headset cable)
- Loudspeaker on / off and control button
- Button "< -". Decrease, left arrow, PgDown
- Button "+ >". Increase, right arrow, PgUp
- Button A. Click, left control button, headset PTT button for radio
- Button B. Context menu, Shift, right control button, Photo, other assigned functions
- Buttons A+B simultaneously start / stop video record
Software controls
- Voice assistant
- Machine learning (AI) algorithms are used to recognize the meaning of user commands, not necessarily the exact pronunciation of the voice command, including the ability to adapt to the voice and pronunciation of the user
- Gesture control
- The stereo camera captures the image of the hands and recognizes the user's gestures (more details on the Hand Tracking page)
- Gesture library constantly updated, Machine Learning allows the user to create custom gestures
- Gestures can indicate not only the state, but also the dynamics, for example, smoothly change the volume level, brightness, etc.
- Capturing and recognizing fingers allows to use software interface controls, including scrollbars, buttons (and a virtual keyboard if necessary), swipe sideways and up or down, scale and rotate screens inside a window, hide and move windows
Perception hardware
The advantage of this wearable and inexpensive device for tactical use by almost every military person is the ability to perceive light, sound and radio waves, inaccessible to humans.
Cameras
- Image capture with a three-sensor front stereo camera. One objective lens transmits the image to the separation prisms and then to 3 sensors: DSLR IR-cut 4K/8K/12K UHD, SenSWIR, HDR
- Separate camera in the range of LWIR (thermal image vision)
- Separate rear view camera with extended visible light and SWIR
- Folded optical lenses design
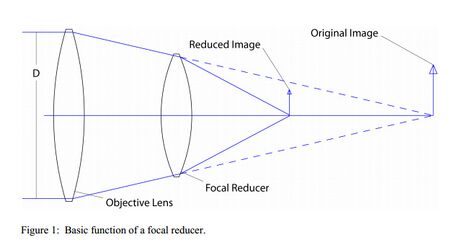
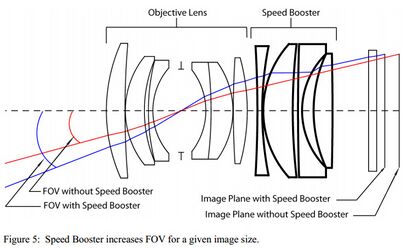
- Built-in Speed Booster reduces focal length and increases aperture for individual sensors
- Built-in teleconverter, on the contrary, increases the focal length for other sensors, increasing the image of distant objects
- IR filter laser protection lens coating for 700-1080 nm (against systems for remote detection of optical and optoelectronic devices)
- Infrared and laser light sources are not used in this device, because this demasks the user
Microphones
- Built-in MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical-Systems) microphone (1) in mask obturator airway to transmit the user's voice
- If the lower part of the mask is not used, a boom microphone (2) with a windproof pad on the flexible goosneck is connected
- 19 external MEMS cardioid microphones, "flat/dome" acoustic arrays allow to perceive sound waves in a wide range of frequencies, including those inaudible to humans, from very low to very high, used in Computer Audition modes (CAC)
- incl. Gunfire Locator
- incl. Active noise reduction (MMC)
- The super-cardioiod and ultra-cardioid microphones with a narrow directivity pattern on the front of the mask allow to accurately determine the source of the sound wave
- 2 insulating layers, airway obturator and seal around face make the user's voice almost inaudible from the outside
Radio antennas
- Built-in transmit-receive antennas in the ranges of the near radius of communications (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE, 5G)
- Integrated manpack antennas for communications in the VHF, UHF, UHF SAT, MUOS, L/S bands
- Integrated manpack antennas for analyzing and listening to the frequency ranges 2 MHz - 8 GHz
- Not every user needs a separate antenna or a set of several antennas with different characteristics, using the P2P network within the group, packets of messages and received data can be exchanged and routed
- Integrated passive radar antenna with active phased array (installed in NVG mount)
- Integrated handheld portable short-range active metal re-radiation radar antenna
- Integrated receiving antenna for radar warning system
- Integrated antenna for remote control of a drone or robot
- Integrated antenna for close-range remote control of an active phased array radar (portable or vehicle-mounted)
- Software-defined (reconfigurable) antenna (installed in NVG mount and the other two via the picatinny rails on the sides of the helmet)
- The software-defined antenna is capable of combining the functions of most integrated antennas
The specific is that when using a separate optical lens for each sensor on the left and right, there is a problem of parasitic multi-angle, which will have to be constantly leveled by software, which affects the accuracy of binocular stereo vision. If in a smartphone this is not critical, and there may be 4-8 cameras with their own optics, then for tactical tasks this is of great difficulty. In this case, on the left and right, it is necessary to accurately hold the horizontal distance between the lines of sight for each pair of sensors and position them vertically, and then programmatically compensate for the vertical shift in order to reproduce a single optical axis for the left and right channels. In addition, the design of the device should allow this to be done without difficulty, including taking into account the angle of the field of view of the optics and solving the problem of shadowing.
Menu items description
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
→redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
The menu has 7 functional sections:
- Status bar (SB)
- Left main menu (LMM)
- Right submenu (RSB)
- Left quick menu (LQM)
- Right quick menu (RQM)
- Left features sidebar (LFS)
- Right features sidebar (RFS)
The principle of managing menu items of some sections is the same, and some are different.
Status bar (SB)
The status bar is located in the top middle of the visible area and contains all the main and frequently used information about the use of device functions and applications.
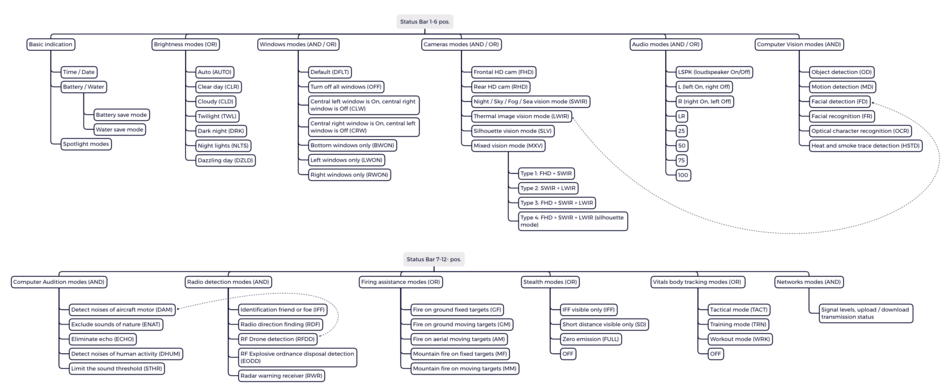
A total of 12 items for quick selection and tracking are available in the status bar, each of which contains sub-elements responsible for specific function presets. Preset settings are carried out not through the status bar, but in the settings of services or applications. The status bar is always displayed and is not hidden. Each element is located in a separate field (fading pad).


The sub-elements of the status bar are controlled by clicking (joystick, gesture control) or by voice (the result corresponds to the click). Default states:
- Hover state: 4 corner segments of the field frame (in the above example in the "Radio Detection modes" field with the "IFF" function)
- Click state: frame on the border of the field (animation effect, twice 100 ms), with each click sequenced display of list elements (presets)
- Selected (long click >2 s): vertically positioned rectangle in the lower left corner
- Not selected (long click >2 s): no vertical rectangle in the lower left corner
Differences in voice control:
- The command to the voice assistant contains a description of the desired action and state, so it is faster
- The voice assistant understands different interpretations of actions and states, so there is no need to memorize voice commands
SB indication and change of display
SB Presets
| Indication | Field name | Preset | Preset name | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time / Date, Battery, Water, Spotlights modes | na | Time / Date |
| |
| na | Battery |
| ||
| na | Water |
| ||
| na | Spotlight |
| ||
| Brightness modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
AUTO | Auto |
| |
| CLR | Clear day | fading pads 50%, fading windows 50%, projector beam 100% | ||
| CLD | Cloudy | fading pads 25%, fading windows 25%, projector beam 75% | ||
| TWL | Twilight | fading pads 0%, fading windows 0%, projector beam 75% | ||
| DRK | Dark night | fading pads 0%, fading windows 0%, projector beam 50% | ||
| NLTS | Night lights | fading pads 50%, fading windows 25%, projector beam 75% | ||
| DZLD | Dazzling day | fading pads 75%, fading windows 75%, projector beam 100% | ||
| Windows modes
AND / OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case cancels, and in the other case does not cancel the selection of the previously selected preset) |
DFLT | Default | displays all active windows according to the configured application and feature priorities; DFLT - deselects any previously selected preset | |
| OFF | Turn off all windows | turns off the display of all windows; OFF - deselects any previously selected preset | ||
| CLW | Central left window is On, central right window is Off | if both central windows (left and right) were used by default, disables the central right window, all functions remain available in the central left window; CLW cancels CRW and vice versa | ||
| CRW | Central right window is On, central left window is Off | as in the previous case, on the contrary, disables the central left window, improving the view of the environment; CRW cancels CLW and vice versa | ||
| BWON | Bottom windows only | turns off the upper windows (except LUW and RUW) on the left and right to improve the view ("knight's narrow visor effect"), transfers higher priority windows to the lower area, closes lower priority windows, does not turn off the central windows; BWON cancels LWON and RWON | ||
| LWON | Left windows only | turns off all windows on the right (except RUW) ("left eye effect"), transfers higher priority windows to the left area, closes lower priority windows, does not turn off central windows; LWON cancels RWON and BWON | ||
| RWON | Right windows only | turns off all windows on the left (except LUW) ("right eye effect"), transfers higher priority windows to the right area, closes lower priority windows, does not turn off central windows; RWON cancels LWON and BWON | ||
| Cameras modes
AND / OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case cancels, and in the other case does not cancel the selection of the previously selected preset) |
FHD | Frontal HD cam | uses visible light range (400-780 nm) and dual sensor capabilities, high resolution and wide dynamic range under strong contrast lighting | |
| RHD | Rear HD cam | turn the rear view camera on and off | ||
| SWIR | Night / Sky / Fog / Sea vision mode | uses a wider short-wavelength infrared light range (780-1700 nm), which is used to observe the reflection of ambient light in this range by objects located on the surface of the water, in fog, in smoke, in clouds, at dusk and at night | ||
| LWIR | Thermal image vision mode | uses long-wavelength invisible infrared light (7.5-14 µm) emitted by objects warmer in relation to the environment, mainly at night | ||
| SLV | Silhouette vision mode | turns on the transformation of the fill into a color outline mode that is well distinguishable in relation to the background for contrasting objects | ||
| MXV1 | Mixed vision mode Type 1: FHD + SWIR | allows to use the capabilities of three different sensors in different conditions day and night; 4K UHD + HDR + SWIR | ||
| MXV2 | MXV Type 2: SWIR + LWIR | allows to use the capabilities of two different sensors in different conditions day and night; SWIR + LWIR | ||
| MXV3 | MXV Type 3: FHD + SWIR + LWIR | allows to use the capabilities of four different sensors in different conditions day and night; 4K UHD + HDR + SWIR + LWIR | ||
| MXV4 | MXV Type 4: FHD + SWIR + LWIR (silhouette mode) | allows to use the capabilities of four different sensors in different conditions day and night; 4K UHD + HDR + SWIR + LWIR (silhouette mode) | ||
| Audio modes
AND / OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case cancels, and in the other case does not cancel the selection of the previously selected preset) |
LSPK | Loudspeaker On/Off |
| |
| L | Left On, right Off |
| ||
| R | Right On, left Off |
| ||
| LR | Left On, right On |
| ||
| 25 | 25% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 25 cancels 50, 75, 100 | ||
| 50 | 50% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 50 cancels 25, 75, 100 | ||
| 75 | 75% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 75 cancels 25, 50, 100 | ||
| 100 | 100% sound level | changes the headphone volume; 100 cancels 25, 50, 75 | ||
| Computer Vision[3][4] modes
AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset) |
OD | Object detection |
| |
| MD | Motion detection |
| ||
| FD | Facial detection |
| ||
| FR | Facial recognition |
| ||
| OCR | Optical character recognition |
| ||
| HSTD | Heat and smoke trace detection |
| ||
| Computer Audition modes
AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset) |
DAM | Detect noises of aircraft motor |
| |
| ENAT | Exclude sounds of nature |
| ||
| ECHO | Eliminate echo |
| ||
| DHUM | Detect noises of human activity |
| ||
| STHR | Limit sound threshold |
| ||
| GFL | Gunfire Locator | is a system that detects and conveys the location of gunfire or other weapon fire using acoustic[2], vibration, optical[3], or potentially other types of sensors, as well as a combination of such sensors. These systems are used by law enforcement, security, military, government offices, schools and businesses to identify the source and, in some cases, the direction of gunfire and/or the type of weapon fired. | ||
| Radio detection modes
AND condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset in one case does not cancel the selection of a previously selected preset) |
IFF | Identification Friend-or-Foe |
| |
| RDF | Radio Direction Finding[6] |
| ||
| RFDD | Radio Frequency Drone Detection[7] |
| ||
| EODD | Radio Frequency Explosive Ordnance Disposal Detection |
| ||
| RWR | Radar Warning Receiver[8] |
| ||
| Firing assistance modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
GF | Fire on ground fixed targets |
| |
| GM | Fire on ground moving targets |
| ||
| AM | Fire on aerial moving targets |
| ||
| MF | Mountain fire on fixed targets (prospective function) |
| ||
| MM | Mountain fire on moving targets (prospective function) |
| ||
| Stealth modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
IFF | IFF visible only |
| |
| SD | Short distance visible only |
| ||
| FULL | Zero emission |
| ||
| OFF | OFF |
| ||
| Vitals body tracking modes
OR condition when selecting presets (selecting one preset cancels the selection of the previously selected preset) |
WRK | Workout mode |
| |
| TRN | Training mode |
| ||
| TACT | Tactical mode |
| ||
| OFF | OFF |
| ||
| Networks modes /
Com status AND |
Signal levels | Network 1, 2, 3, 4 |
Signal levels, upload / download transmission status | |
| online | ||||
| back soon | ||||
| don't disturb | ||||
| offline |
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
→redirect Further information: Public:Applications, Public:Voice User Interface
| Left | Center | Right | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMP | Left main menu fading pads | SBP | Status bar fading pads | RSBP | Right submenu fading pads |
| LQMP | Left quick menu fading pads | CLW | Central left window | RQMP | Right quick menu fading pads |
| LFSP | Left features sidebar fading pads | CRW | Central right window | RFSP | Right features sidebar fading pads |
| LUW | Left Upper window | CWJP | Central window joystick pads | RUW | Right Upper window |
| LTAW | Left Top A window | CWBP | Central window buttons pads | RTAW | Right Top A window |
| LTBW | Left Top B window | RTBW | Right Top B window | ||
| LBAW | Left Bottom A window | RBAW | Right Bottom A window | ||
| LBBW | Left Bottom B window | RBBW | Right Bottom B window | ||
The main menu (LMM) is located at the top left of the visible area and contains a list of sections.
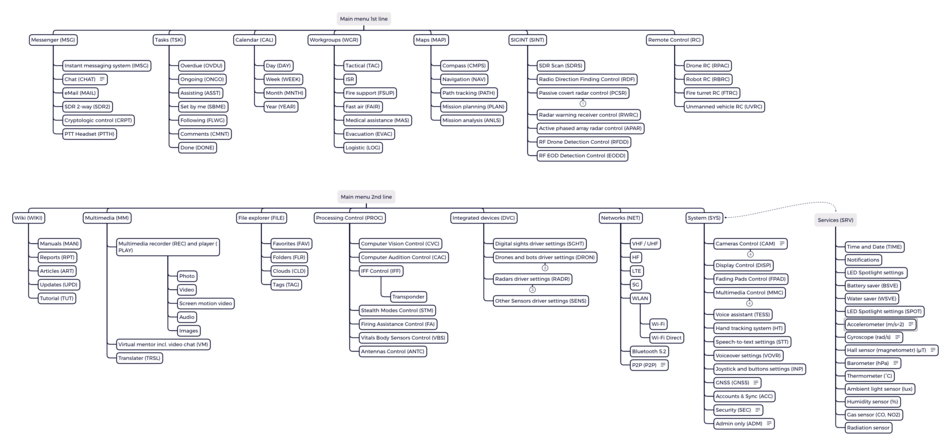
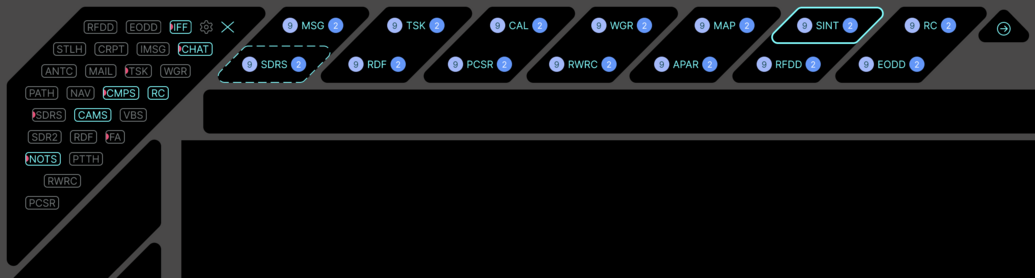
Only 7 elements for quick selection in one row. Use the navigation arrows on the right to select the next row. The main menu is only displayed on hover or on a voice call. When inactive, hides after 15 seconds. Each element is located in a separate field (fading pad). Only the fields that display the section are shown.
The right submenu (RSB) is at the top right and expands the second lower level of the main menu items. Only 7 elements in one row. The arrows on the left are used for navigation. The right submenu is displayed only when one of the main menu items on the left (LMM) is active or when the submenu item is directly called by voice. When inactive, hides simultaneously with the main menu after 15 seconds. Each element is located in a separate field (fading pad). Only the fields that display the section are shown.
When an app is opened using this menu, it is displayed on the screen. If the user closes the app, it does not stop its work, but continues to work in the background, at the same time, an element with the name of this application appears in the Left quick menu (LQM) or Right quick menu (RQM) menu field to quickly return to the screen. See the sections Left quick menu (LQM) and Right quick menu (RQM) below for how to completely terminate the application.
The sub-elements of the main menu and sub-menu are controlled by clicking (joystick, gesture control) or by voice. States:
- Hover state: 4 corner field frame segments
- Click state: frame on the field border (animation effect, twice 100 ms)
- Selected (long click >2 s): horizontally placed two rectangles to the right and left of the caption
- Not selected (long click >2 s): there are no horizontally placed two rectangles to the right and left of the caption
Differences in voice control:
- The command to the voice assistant contains a description of the desired action and state, so it is faster
- The voice assistant understands different interpretations of actions and states, so there is no need to memorize voice commands
- During a voice call, not the entire menu is shown, but the corresponding items of the main menu and submenu
- The user can voice the display of the entire menu
| LMM | RSB | Action | Notice |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSG
(Messenger) |
IMSG (instant messaging system) |
|
|
| CHAT (multichannel chat) |
|
LMM for all channels, RSB and RFS for the corresponding channel:
| |
| MAIL (eMail) |
|
||
| SDR2 (SDR 2-way) |
|
||
| CRPT (cryptologic control) |
|
||
| PTTH (PTT headset) |
|
||
| TSK (Tasks) |
|
The task management system allows you to plan and control the deadline, accuracy, results, and efficiency of tasks. Contains a description, checklist, deadline, actual completion time and elapsed time (including auto-tracking of completion and accounting of elapsed time), notification of the current status, geolocation at the time of completion, task completion confirmation artifacts, attachments, comments |
|
| CAL (Calendar) |
|
The event calendar allows you to plan and coordinate events in advance that require certain time regulations: collective online and offline communications, individual classes and trainings, meetings, training seminars, TDY (temporary duty) trips, and deployments |
|
| WGR (Workgroups) |
|
The submenu contains filters for groups.
You can select a member or group in the appropriate section to communicate, share data, send or request a position. CDI element (Cross-Domain Interaction) |
|
| MAP
(Maps & Navigation) |
CMPS (Compass) |
|
|
| NAV (Navigation) |
|
||
| PATH (Path tracking) |
|
||
| PLAN (Mission planning) |
|
| |
| ANLS (Mission analysis) |
|
| |
| SINT
(SIGINT) |
SDRS (SDR Scan) |
|
|
| RDF (Radio Direction Finding Control) |
|
||
| PCSR (Passive covert radar control) |
|
||
| RWRC (Radar warning receiver control) |
|
||
| APAR (Active phased array radar control) |
|
||
| RFDD (RF Drone Detection Control) |
|
||
| EODD (RF EOD Detection Control) |
|
||
| RC
(Remote Control) |
RPAC (Drone RC) |
|
|
| RBRC (Robot RC) |
|
||
| FTRC (Fire turret RC) |
|
||
| UVRC (Unmanned vehicle RC) |
|
||
| WIKI (Wiki) |
|
Wiki systems are proven to be effective in creating and sharing the knowledge that everyone needs on an almost daily basis. This system allows for to a collection of best practices and improves the process of learning and training, as well as refreshing knowledge from time to time even from experienced users. All sorts of information about the technical arrangement and maintenance of equipment, the organization of processes at military bases, schedules, analysis materials of military experts, etc. Something that will help you become more efficient. Of course, distributed access rights, information protection, and confidentiality are in accordance with current protocols |
|
| MMD (Multimedia) | REC (multimedia recorder)
PLAY (multimedia player) |
|
|
| VM (Virtual mentor incl. video chat) |
|
||
| TRSL (Translater) |
|
||
| FILE (File explorer) |
|
|
|
| PROC (Processing Control) | CVC (Computer Vision Control) |
|
|
| CAC (Computer Audition Control) |
|
||
| IFF (IFF Control) |
|
||
| STM (Stealth Modes Control) |
|
||
| FA (Firing Assistance Control) |
|
||
| VBS (Vitals Body Sensors Control) |
|
||
| ANTC (Antennas Control) |
|
||
| DVC (Integrated devices) |
|
|
|
| NET (Networks) |
|
|
|
| SYS (System) | CAM (Cameras Control) |
|
|
| DISP (Display Control) |
|
||
| FPAD (Fading Pads Control) |
|
||
| MMC (Multimedia Control) |
|
11 embedded microphones:
| |
| TESS (Voice assistant) |
|
||
| HT (Hand tracking system) |
|
||
| STT (Speech-to-text settings) |
|
||
| VOVR (Voiceover settings) |
|
||
| INP (Joystick and buttons settings) |
|
||
| GNSS (GNSS) |
|
||
| ACC (Accounts & Sync) |
|
||
| SEC (Security) |
|
||
| ADM (Admin only) |
|
||
| SRV (Services) |
|
Displays hides (within a frame) and open app windows on the left half of the screen. To completely stop the app, you need to perform a long click and press confirmation in the notification window.
Displays hides (within a frame) and open app windows on the right half of the screen. To completely stop the application, you need to perform a long click and press confirmation in the notification window.
Left features sidebar (LFS)
Displays:
- functional buttons of some active apps in the left half of the screen, when there are a lot of them and it is undesirable to reduce the visible area of the application window
- list of priority tasks for the TSK application
- list of recently viewed articles for the WIKI app
- list of peer-to-peer leads for P2P application and their real-time characteristics
- priority channel list for WGR application
Right features sidebar (RFS)
Displays:
- function buttons of some active apps in the right half of the screen, when there are a lot of them and it is undesirable to reduce the visible area of the application window (for example, SDRS)
- CHAT app dialog list and dialog filters
- list of recent commands via the IMSG app
- list of taken photos and videos for the PLAY application
- list of video conferencing participants for VM application
Virtual control tools
Displays:
- Software (duplicated and synchronized with hardware) joysticks and buttons for controlling a drone, robot, turret, unmanned vehicles
- Software buttons for controlling cameras of drones, robots and unmanned vehicles
- Joysticks and buttons to control the movement of positions on the map and mark waypoints
- Multimedia control and navigation buttons
Windows items description
![]() →redirect Further information: Public:Applications
→redirect Further information: Public:Applications
Fading windows and pads
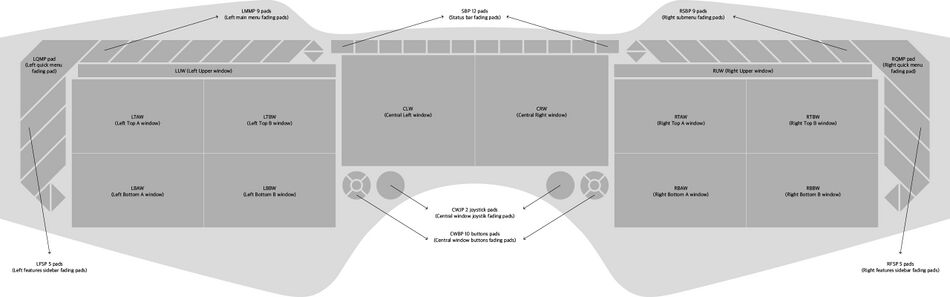
| Left | Center | Right | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMMP | Left main menu fading pads | SBP | Status bar fading pads | RSBP | Right submenu fading pads |
| LQMP | Left quick menu fading pads | CLW | Central left window | RQMP | Right quick menu fading pads |
| LFSP | Left features sidebar fading pads | CRW | Central right window | RFSP | Right features sidebar fading pads |
| LUW | Left Upper window | CWJP | Central window joystick pads | RUW | Right Upper window |
| LTAW | Left Top A window | CWBP | Central window buttons pads | RTAW | Right Top A window |
| LTBW | Left Top B window | RTBW | Right Top B window | ||
| LBAW | Left Bottom A window | RBAW | Right Bottom A window | ||
| LBBW | Left Bottom B window | RBBW | Right Bottom B window | ||
As it was already written at the very beginning of the description of the user interface, fading windows and pads are used in the device for contrast display. Otherwise, on a light and bright background of the environment, it will be difficult for the user to see images with contrast. Fading windows and pads, depending on the brightness modes, have different degrees of transparency. And in the case of bright light, they additionally perform the function of a sun screen.
App windows are placed in a larger and better viewable area. There are 12 independent windows in total (8 large 1.78:1, 2 large 1.20:1, 2 small 19.86:1), each containing control elements when the window is clicked or voice selected (selected state). A non-selected window is a passive window that only displays app graphics, window control elements can be hidden, app control elements can be hidden. Windows of different apps have different display priority, which is configured in the system settings for each application. Depending on the selected preset in the Status bar (SB), the configurations of the displayed windows can be quickly and flexibly changed by the user.
(!) Insert gallery with pictures of examples
Window subelements are controlled by clicking (joystick, gesture control) or by voice. States:
- Hover state: thick dotted line along field border
- Click state: frame on the field border (animation effect, twice 100 ms)
- Selected (long click >2 s): sparse dotted line along field border
- Not selected (long click >2 s): no dotted line
Differences in voice control:
- The command to the voice assistant contains a description of the desired action and state, so it is faster
- The voice assistant understands different interpretations of actions and states, so there is no need to memorize voice commands
The user can quickly and flexibly control the window configuration for each window individually:
- The user can force close any window at any time by selecting the desired window (selected state), clicking on the "close window" icon (the app remains in the background, the app window is in a hidden mode, to reverse the action, click on the icon in the quick selection menu)
- The user can maximize the left or right central window (CLW, CRW) to the entire area of the central window (CW) (merged window will be 2.40:1) by selecting the desired window (selected state), clicking on the "maximize window" icon
- The user can maximize the left or right window (LTAW, LTBW, LBAW, LBBW, RTAW, RTBW, RBAW, RBBW) to the entire left or right area of the window (LW or RW) (merged window will be 1.78:1 x2) by selecting the desired window (selected state), clicking on the "maximize window" icon
- When you click on the "minimize window" icon, the window returns to its original state
- The "move window left" icon moves a window to the left, then up to the right, then to the left, changing the position of other windows
- The "move window right" icon moves a window to the right, then down to the left, then to the right, rearranging other windows
- The "share screen" icon allows you to send a screenshot of a window or enable broadcasting of this window for another user
Apps priority for windows
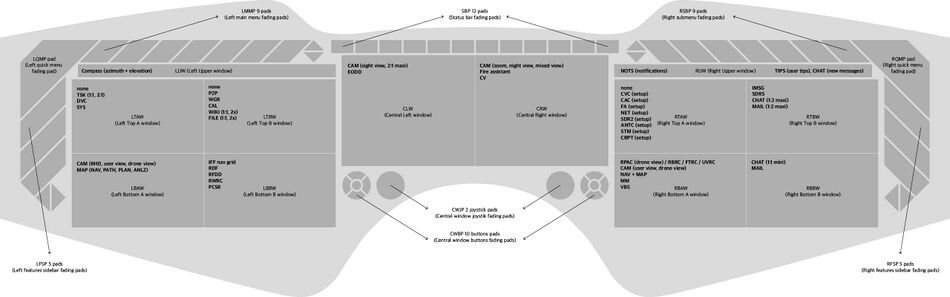
| LUW | CLW | CRW | RUW | ||
|
|
|
| ||
| LTAW | LTBW | CWJP (left) | CWJP (right) | RTAW | RTBW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| LBAW | LBBW | CWBP (left) | CWBP (right) | RBAW | RBBW |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Window | Mode | Notice |
|---|---|---|
| Left Upper window (LUW) | Usually used for a long time | |
| Left top A window (LTAW) | Used when necessary, not recommended during intense combat so as not to limit the visibility of the environment | |
| Left top B window (LTBW) | Usually used for a short time so as not to restrict the visibility of the environment | |
| Left bottom A window (LBAW) | Usually used for a long time | |
| Left bottom B window (LBBW) | Usually used for a long time | |
| Central left window (CLW) | Usually used for a short time so as not to restrict the visibility of the environment | |
| Central right window (CRW) | Usually used for a long time | |
| Right Upper window (RUW) | Usually used for a long time | |
| Right top A window (RTAW) | Usually used for a short time so as not to restrict the visibility of the environment | |
| Right top B window (RTBW) | Used when necessary, not recommended during intense combat so as not to limit the visibility of the environment | |
| Right bottom A window (RBAW) | Usually used for a long time | |
| Right bottom B window (RBBW) | Usually used for a long time |
Movement of windows to the left and right
- General rule "left to right, top to bottom" (list moving of 10 windows):
- LTAW - left top window A
- LTBW - left top window B
- LBAW - left bottom window A
- LBBW - left bottom window B
- CLW - central left window
- CRW - central right window
- RTAW - left top window A
- RTBW - left top window B
- RBAW - left bottom window A
- RBBW - left bottom window B
- If the active window is on the left side and it moves to the left, it moves up the list
- If the active window is on the left side and it moves to the right, it moves down the list in the left side, then from the left to the right in the center of the screen, then moves down the list in the right side
- If the place where the active window is moved is not occupied by another window, other windows do not change their position
- The other displayed window that the active window is moved down the list to is automatically moved up the list and takes the previous position of the moved active window
- The other displayed window that the active window is moved up in the list to is automatically moved down the list and takes the previous position of the moved active window
- Typically less than 10 large windows are displayed at the same time, so moving the active window does not move most other windows
- If all 10 large windows are displayed, move the active window by several positions in the list causes the neighboring window to be sequentially automatically temporarily moved, which then returns to the previous position again
- If the window is maximized and need to move, it is automatically minimized and moved according to the general rule, if necessary, it must be maximized manually again
- The user can select two or more windows at the same time by holding down the D key (near the joystick) right headphones ear cup (similar to the right mouse button)
- By selecting a window and holding down the C key (similar to the left mouse button) right headphones ear cup, the user can move the window or several windows at the same time with one action using the joystick - in this case, if a group of windows is moved, they will be located sequentially next to the list (even if in their previous location, they were not sequentially next to each other in the list)
- Small windows (LUW and RUW) move only to the left or right in place of a similar small window
- If the small window is moved to the right, the other window is moved to the left (swap)
- If an app launches a small window while both small windows are displaying information from other applications, then the window with the app with the lowest priority is hidden in the shortcut menu (LQM or RQM)
- If one small window closes, nothing is displayed in its place, to display the window of another app in this place, you need to click on it in the quick menu (LQM or RQM) or in the main menu (LMM and then RSB)
- If an app launches a window that has a higher priority than an already occupied window, then the lower priority window is moved to another location, as dictated by the window and app priority rules. When closing a window with a higher priority, the window configuration returns to the previous state
- If an application launches a window when there is no free more space to display windows, the window with the lowest priority is hidden automatically in the quick menu (LQM or RQM). When you close one of the windows with a higher priority, the previous window display state is restored. If you need to display a window with a lower priority, you need to make free space for it by minimizing one of the windows in the quick menu (LQM or RQM)
Scrolling the window by (4/5 of the window height or in rows - adjustable individually) is done using the up and down icons (scrollbar) or the joystick buttons "< +" and "->" from the bottom of the left or right headphones ear cup (similar to the PageUp, PageDown mouse buttons). Also smooth scrolling of the window with a joystick, voice command or gesture (including a virtual joystick or a separate gesture).
Window control icons, app control icons, app interface buttons located on the Left Features Sidebar (LFS) or Right Features Sidebar (RFS), virtual joysticks - refer only to the active (selected) window. For a passive window (not selected), they are not displayed. The exceptions can be customized, for example CHAT icons in RFS.
Separately for the window control icons - after the window has become active (selected), the window control icons are displayed for 15 seconds, after which they disappear (it can be in the settings disabled). To re-display them, select this window again. The active window's dotted highlight box is displayed for the duration of the window's active state.
For the not selected state you can click on another place on the screen or press the D button on the right headphones ear cup without click.
Also, forced use of some windows can act as a sunshield when the sun is low on the horizon in the line of sight. The user can move the window to the desired area and block the dazzling view of the sun without fading the entire viewing area.
Interface Animation
Interface items motion
- common view
- active view when working with the menu
- the process of selecting a menu item (scrolling elements, changing the view when entering the submenu)
- permanent (continuous) view (statuses, notifications, active menu items)
- turning on and changing fading windows (rules, combination options in a simultaneous form)
Modern tools
- Qt + C++ (doc, wiki, quick start, framework modules, 6.2.4, QML, Qt Habr, Qt for Startups, Open Source Licences, download for GNL3 Open Source)
- Electron.JS + React.JS + TypeScript
- MRTK-Unity is a Microsoft-driven project that provides a set of components and features, used to accelerate cross-platform MR app development in Unity. Here are some of its functions:
- Provides the cross-platform input system and building blocks for spatial interactions and UI.
- Enables rapid prototyping via in-editor simulation that allows you to see changes immediately.
- Operates as an extensible framework that provides developers the ability to swap out core components.
- Supports a wide range of platforms.
- Unity Mars helps solve the hard problems of AR app creation:
- Overcome the challenges of authoring for dynamic physical environments
- Reduce development time
- Release cross-platform experiences with support for iOS, Android, and HoloLens
Manuals
Troubleshooting
Areas of research
Related fields
Future ideas
Further reading
See also
| Public External Sections: | Public Wiki Sections: | Public Wiki Sections: | Not-Public Wiki Sections: |
|---|---|---|---|
Note: Unless otherwise stated, whenever the masculine gender is used, both men and women are included.
See also product details
| Hardware Details: | Functional Apps Details: | Executive Apps Details: | Service Apps Details: |
|---|---|---|---|
References
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Field of view"
- ↑ GitHub, Pimax Forum, "HMD Geometry Database"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Outline Computer Vision"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Computer Vision"
- ↑ Wikipedia, Artillery sound ranging
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Radio direction finding"
- ↑ AARTOS, "RF Drone Detection", "Antennas"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "List of radar types", "Counter-battery radar"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Counter-battery radar"
- ↑ Wikipedia, "Monitoring (medicine)"